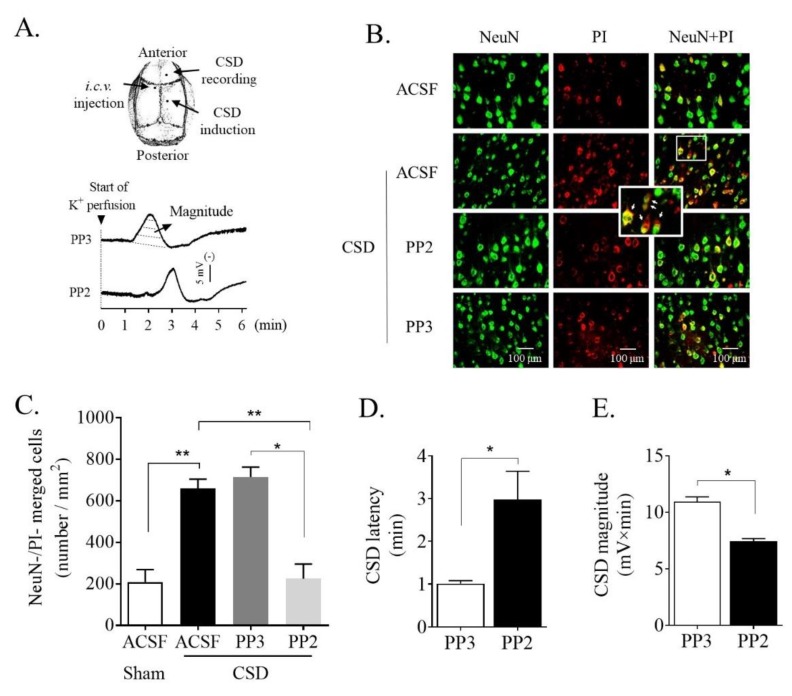
Figure 1.
PP2, the SFK selective inhibitor, perfused into contralateral i.c.v. attenuated CSD-induced neuronal PI staining in the ipsilateral cortex of rat and reduced cortical susceptibility to CSD. (A) Schematic drawing shows cranial preparation and representative traces showing CSD propagation wave after i.c.v. perfusion of 2.5 nmol PP2 or its negative analog PP3. CSD magnitude (mV × minute, dashed area) and latency (L, minute) were used for quantifying CSD. (B) Representative images of CSD-induced PI staining (red) of NeuN positive cells (green) in layers V and VI of the sensorimotor cortices treated with ACSF, 2.5 nmol PP3 or PP2 in the absence or presence of 3M K+-induced CSD. PI and NeuN positive cells (yellow) indicated by arrows shown in the inset indicated increased Panx1 activity. (C) Effects of PP2 (n = 4) or PP3 (n = 4) on PI staining indicated by the number of merged cells (cells/mm2). CSD group (n = 5) and sham group (n = 6) were used as controls. (D,E) Effects of PP2 (n = 4) and PP3 (n = 4) on CSD latency and magnitude. Kruskal–Wallis test for comparison among multiple groups, followed by one-tailed Mann–Whitney test for comparisons between 2 independent groups. All the values shown are means ± SEM. Significant differences were set when * p < 0.05 or ** p < 0.01.