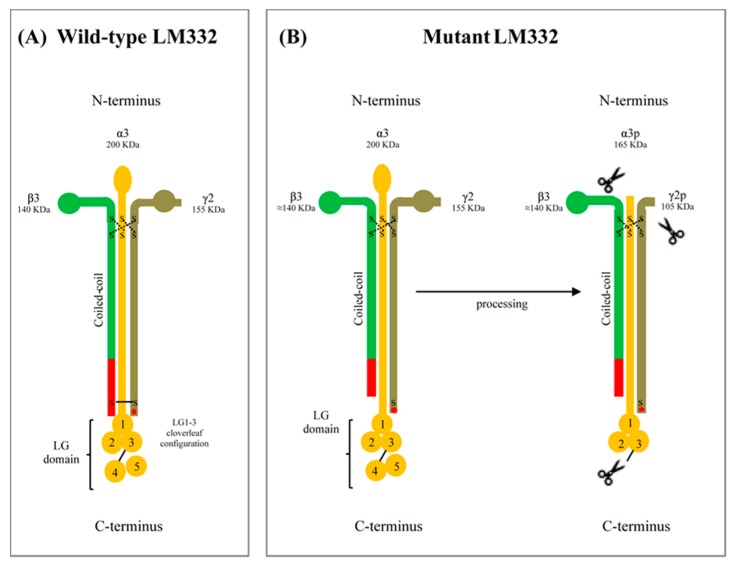
Figure 4.
Schematic of the laminin-332 (LM332) structure and its maturation process. (A) Unprocessed, intracellular form of the wild-type LM332. It consists of three chains: α3 (200 kDa), β3 (140 kDa) and γ2 (155 kDa). These chains fold together in a coiled coil cross. The heterotrimeric molecule is stabilized by disulphide bonds at the N-terminus (dashed lines) and C-terminus. The C-terminal bond connects Cys1171 in the β3 chain to Cys1184 in the γ2 chain (solid line). (B) Left panel. Unprocessed, intracellular form of the mutant LM332 of our patient. Mutation p.Cys1171* in the β3 chain results in absence of the disulphide bond at the C-terminus. (B) Right panel. Processed, extracellular form of the mutant LM332. Similar to the wild-type form, the mutant LM332 is normally secreted and proteolytically cleaved within the α3 and γ2 chains (cleavage sites are indicated by scissors), and then deposited in the extracellular matrix. The maturation process of LM332 outside the cells determines the reduction of α3 chain size from 200 to 165 kDa (α3p), and of γ2 chain from 145 kDa to 105 kDa (γ2p). The last 20 C-terminal residues of the β3 chain (red trait) and Glu1191 in the γ2 (red dot) that are important structural determinants for integrin recognition are indicated.