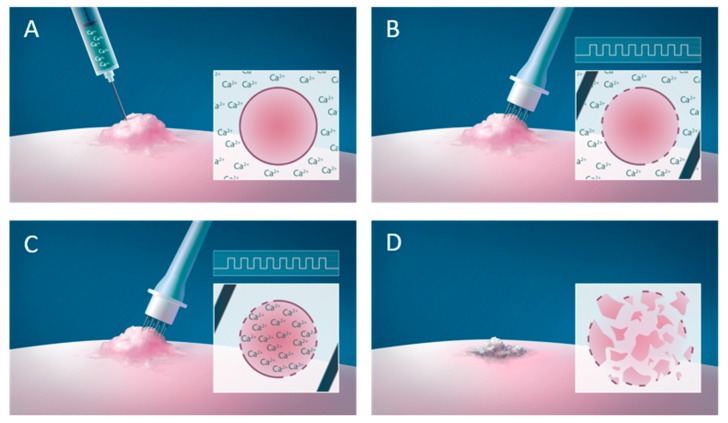
Figure 1.
Calcium electroporation. (A) Calcium is injected in the tumor causing a high extracellular calcium concentration. (B) Immediately after the injection, the tumor is electroporated using an electrode (e.g. needle electrode) causing transient permeabilisation of the cell membrane allowing passage of calcium into the cell (C) causing cancer cell death (D).