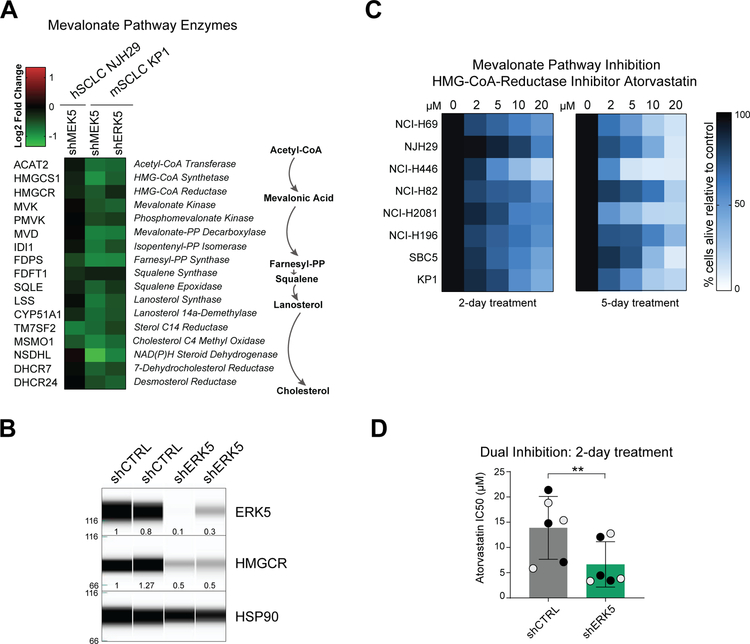
Figure 5: MEK5 and ERK5 knockdown results in inhibition of the mevalonate pathway and increased sensitivity to mevalonate pathway inhibitors.
(A) MEK5 and ERK5 knockdown cells downregulate Mevalonate pathway enzymes (biosynthesis schematic on right) compared to cells infected with shCTRL hairpins (from RNAseq FPM values).
(B) Immunoassay for ERK5, HMGCR, and HSP90 expression in control and ERK5 knock-down NHJ29 hSCLC cells. The molecular weights are indicated on the left (in kDa). The amount of ERK5 and HMGCR relative to the first control and to HSP90 are indicated below the signal corresponding to each protein.
(C) Treatment of 8 SCLC cell lines (7 human cell lines and the mouse cell line KP1) with increasing doses of atorvastatin in reduced (2%) serum media; color corresponds to % cells alive compared to vehicle-treated controls after 2 or 5 days at each concentration; n=3 independent experiments per treatment.
(D) Concentrations of atorvastatin necessary to kill 50% of NHJ29 cells (IC50) infected with shCTRLs are higher than concentrations needed to kill cells with ERK5 knockdown; grey and black dots represent two independent hairpins per group; n=3 experiments, **, p≤0.005 (t-test).