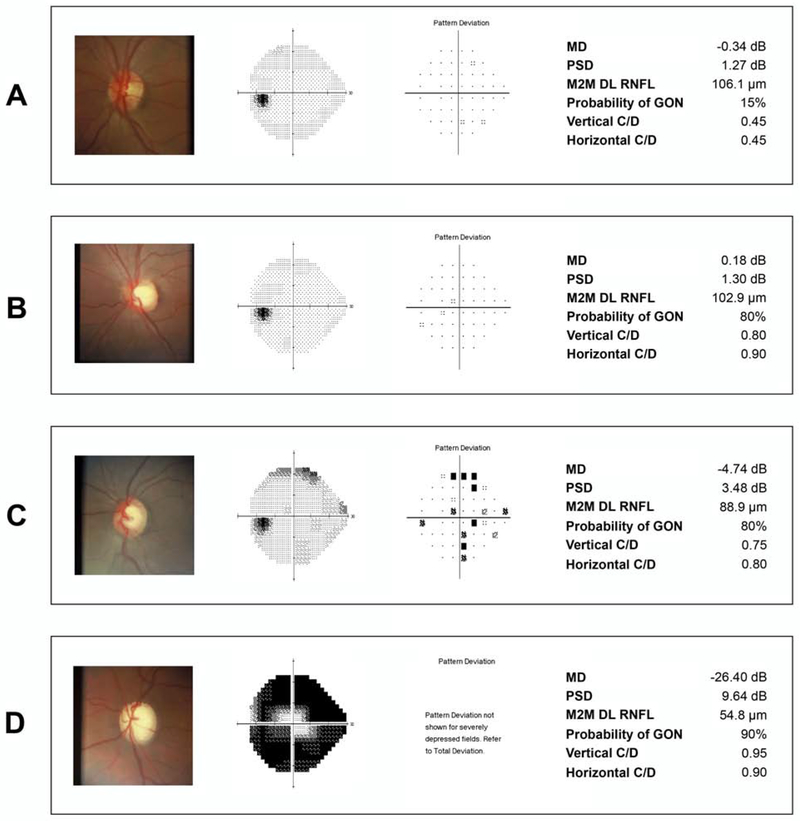
Figure 4.
Examples of eyes included in the study. (A) shows an eye with normal visual field and normal appearing optic disc. The human graders gave a low probability of glaucomatous optic neuropathy (GON) (15%), which agreed to the thick retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness predicted by the machine to machine (M2M) deep learning (DL) algorithm. (B) shows an eye with a large but likely physiologic cup given the healthy appearance of the RNFL. The DL prediction indicated a thick RNFL, whereas human graders seemed to have overestimated the probability of GON. (C) shows an eye with early glaucomatous visual field loss where the DL algorithm predicted a thinner RNFL and human graders also gave a high probability of GON. Finally, (D) shows an eye with advanced visual field loss where the DL thin predicted RNFL agrees with the high probability of GON given by human graders.