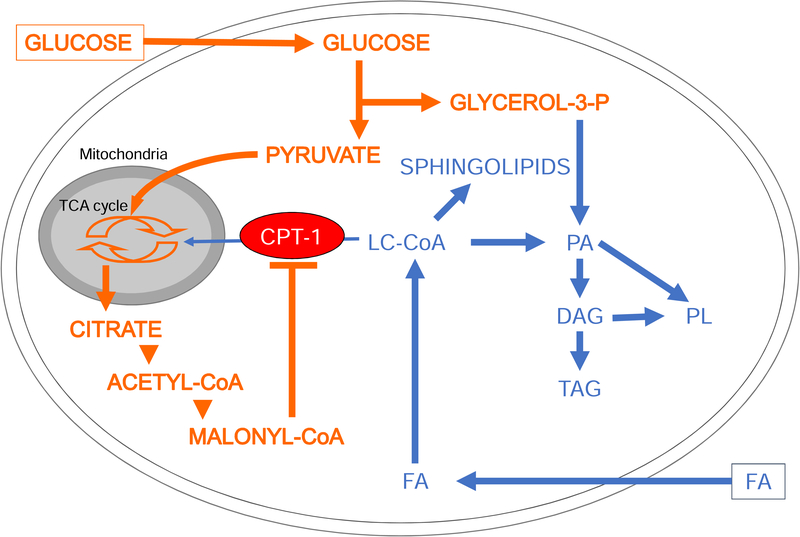
Figure 5: Effects of glucose on intracellular lipid metabolism in the β-cell.
In the presence of simultaneously elevated levels of glucose and FFAs, the increase in cytosolic malonyl-CoA resulting from glucose metabolism inhibits carnitine-palmitoyl transferase 1 (CPT-1). Transport of long-chain acyl-CoA (LC-CoA) in the mitochondria is blocked, and FFA metabolism is diverted towards the synthesis of lipid-derived signaling molecules such as sphingolipids, diacylglycerols (DG), phosphatidic acid (PA), phospholipids (PL) and triacylglycerols (TG). Adapted from [51] with permission.