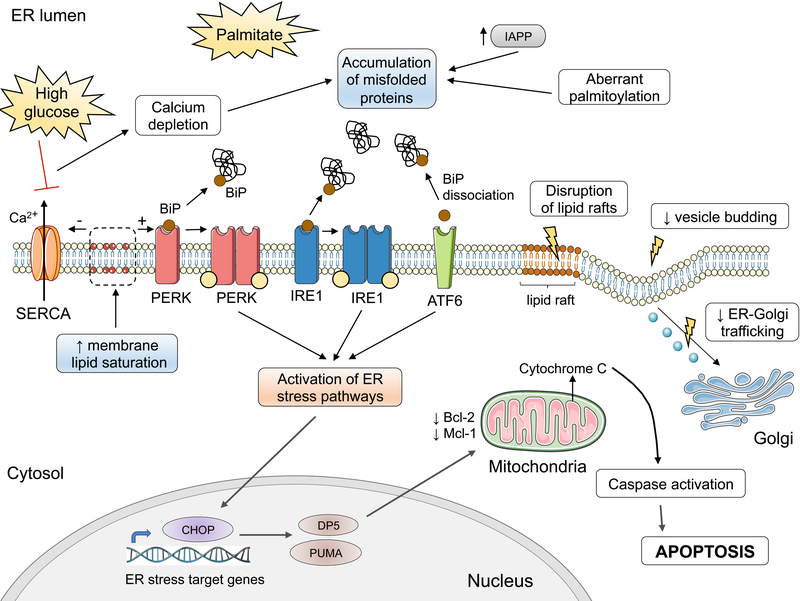
Figure 7: Activation of ER stress pathways by palmitate.
Exposure of β-cells to palmitate induces aberrant protein palmitoylation and Ca2+ depletion in the ER, affecting ER folding capacity. The depletion of Ca2+ stores is aggravated by the downregulation of the sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) pump in high glucose conditions. In parallel, palmitate disrupts the export of cargo from the ER and trafficking to the Golgi, contributing to the buildup of unfolded or misfolded proteins. The misfolded proteins recruit the ER chaperone BiP, causing its dissociation from the luminal domain of the ER stress transducers PERK, IRE1 and ATF6. This, together with increased ER membrane lipid saturation, results in the activation of the ER stress transducers, eliciting downstream ER stress signaling. This in turn leads to the induction of the proapoptotic proteins CHOP, PUMA and DP5, the latter inhibiting anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family. These events culminate in mitochondrial permeabilization, cytochrome C release and mitochondrial apoptosis. Graphic elements used in this illustration come from Servier Medical art (https://smart.servier.com).