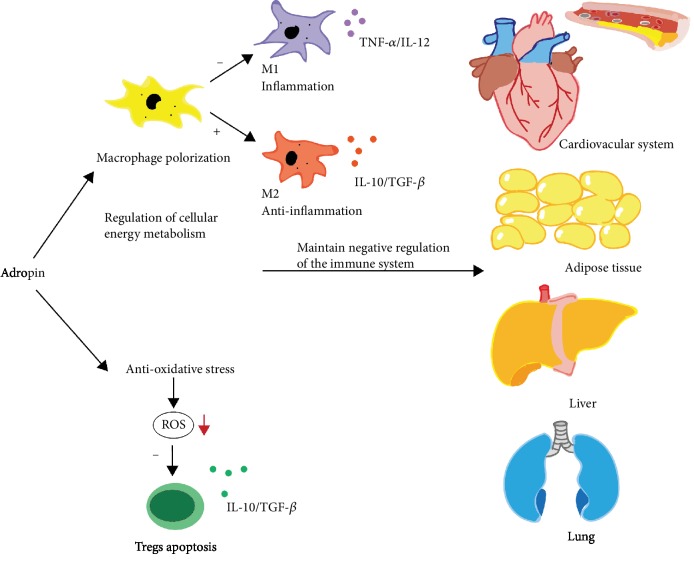
Figure 3.
Adropin plays an anti-inflammatory role in a variety of tissues. Adropin can affect macrophage polarization by regulating cell energy metabolism and prevent ROS-induced apoptosis of Tregs through antioxidant stress. Thus, it can maintain the negative regulation of the immune system and play an anti-inflammatory role in atherosclerosis, fat inflammation, fatty liver, nonalcoholic hepatitis, and pulmonary vasculitis. Adropin deficiency can lead to imbalance of immune cells and inflammatory cytokines, which will destroy the negative regulation of the immune system and result in inflammation.