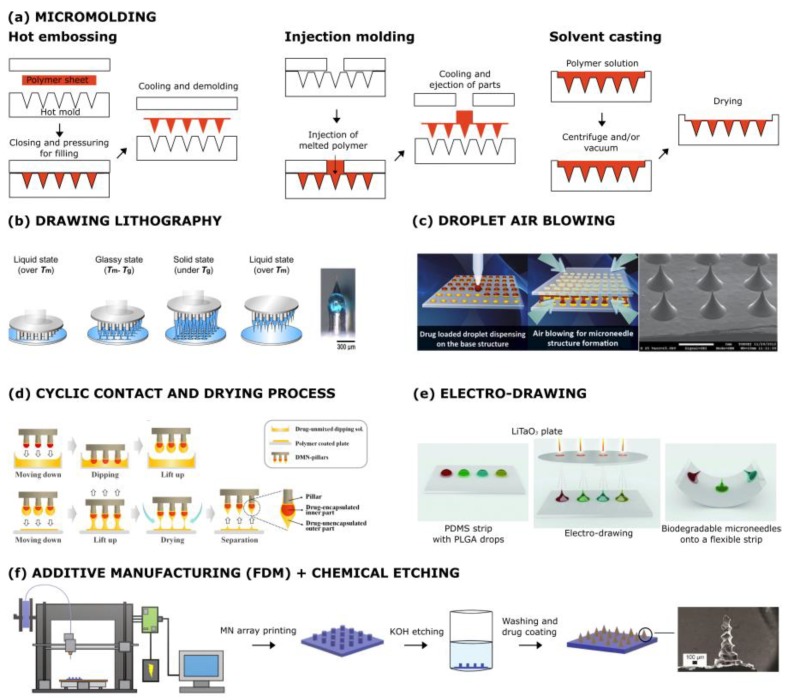
Figure 1.
Microneedle (MN) manufacturing methods. (a) Micromolding: The mold with the desired MN structures can be filled with polymers by hot embossing, injection molding, or solvent casting. (b) Drawing lithography: The polymer is melted, dispensed on a fixed plate, and elongated by pillars in the upper-moving plate. (c) Droplet air blowing: Two plates, with polymer drops within, are contacted and then moved. When the final distance between the plates is reached, the polymer is hardened by means of air blowing. (d) Cyclic contact and drying: Pillars are repeatedly contacted with a drug-polymer solution, lifted, and dried with air blowing. (e) Electro-drawing: A thermal stimulus is applied to a pyroelectric crystal, generating an electric field which drives the microneedle drawing process. (f) Fused deposition modeling (FDM) of biodegradable polymer MNs: FDM is followed by KOH etching to improve feature size. Reprinted with modification from [36,37,38,39,40,41].