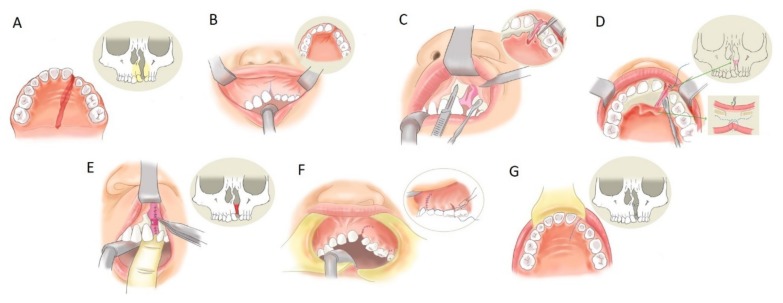
Figure 1.
Extensive gingivoperiosteoplasty. Alveolar cleft and bone defect (A). Incision line made on the upper gingiva along with the cleft (B). The gingival mucoperiosteal flap, in which the blood supply comes from the superior part, was elevated to explore the cleft (C). The palatal mucoperiosteal flap deep to the margin of the alveolar fistula was elevated (D). Then, the tissue of the nasal floor was watertight sutured (E). The bone graft was packed into the cleft area at this step (secondary alveolar bone grafting (SABG) method). The gingival site and palatal site wound were closed completely (F,G).