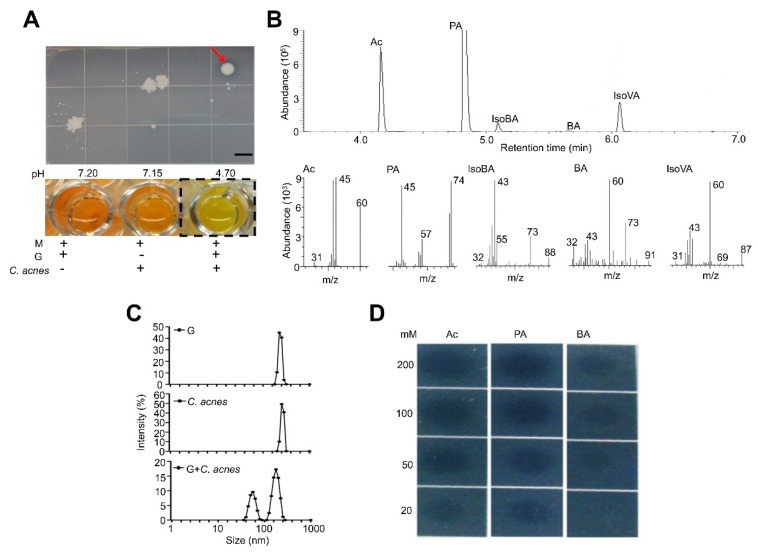
Figure 1.
The CaP-solubilizing property of C. acnes and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in fermentation media. (A) A CaP-solubilizing skin microorganism developing a clear zone (red arrow) was identified as C. acnes, which used 2% glucose (G) in a CaP-rich Pikovskaya’s agar to undergo fermentation. The pH values of phenol red-containing media with glucose, C. acnes, and glucose plus C. acnes were 7.20, 7.15 and 4.70, respectively. Scale bar = 1 cm. (B) Spectra of gas chromatography (GC) and mass spectrometry (MS) of five SCFAs produced by glucose fermentation of C. acnes were displayed. Fragment ions (m/z) for each SCFA were indicated. Ac, acetic acid; BA, butyric acid; IsoBA, isobutyric acid; IsoVA, isovaleric acid; PA, propionic acid. (C) The size of CaP was determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) after incubation of CaP with culture media of glucose alone, C. acnes alone or glucose plus C. acnes. (D) Different concentrations of Ac, BA, and PA were added onto the CaP-rich Pikovskaya’s agar plates. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown.