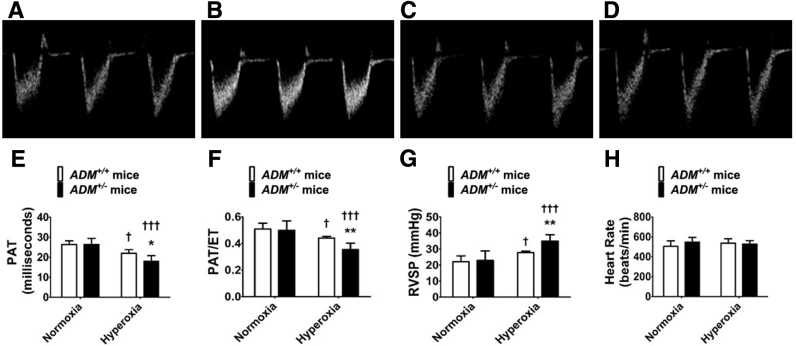
Figure 4.
Indexes of pulmonary hypertension at postnatal day (PND) 28 in adrenomedullin-deficient (ADM+/−) mice exposed to neonatal hyperoxia: High-resolution echocardiographic studies were performed at PND28 on adrenomedullin-sufficient (ADM+/+) or ADM+/− mice exposed to 21% oxygen (normoxia) for 4 weeks or 70% oxygen (hyperoxia) for 2 weeks followed by normoxia for 2 weeks. A–D: Representative pulsed-wave Doppler (PWD) echocardiographic recordings of pulmonary artery blood flow obtained from ADM+/+ (A and C) and ADM+/− (B and D) mice exposed to normoxia (A and B) or neonatal hyperoxia (C and D). E–H: Pulmonary acceleration time (PAT) (E), PAT/ejection time (ET) ratio (F), right ventricle systolic pressure (RVSP) (G), and heart rate (H) were estimated from the PWD echocardiographic recordings of the pulmonary artery blood flow. Data are expressed as means ± SD. n = 4 to 8 mice per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus ADM+/+ mice; †P < 0.05, †††P < 0.001 versus normoxia.