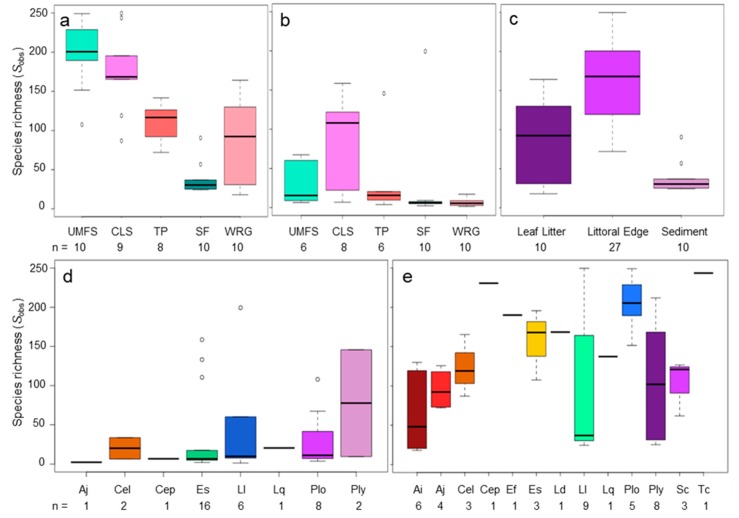
Figure 3.
The observed species richness (Sobs) in the gut microbiomes of dragonflies grouped by life stage and site, habitat, or species. Sobs is calculated as the number of operational taxonomic units detected when subsampling 453 16S rRNA gene sequences from each sample over 1000 iterations. Sobs is represented as boxplots with quartiles, including median line, outliers (circles), and whiskers representing the minimum and maximum Sobs for each sample type. (a) Dragonfly nymphs at sites representing a gradient of potential human impact (WRG>SF>TP>CLS>UMFS); (b) dragonfly adults at sites representing a gradient of potential human impact (WRG>SF>TP>CLS>UMFS); (c) dragonfly nymphs collected from different aquatic microhabitats, representing leaf litter, plants in the littoral edge, or sediment; (d) dragonfly adults separated by species; and (e) dragonfly nymphs separated by species. Species were identified as Anax imperator (Ai), Anax junius (Aj), Celithemis elisa (Cel), Celithemis eponina (Cep), Erythemis simplicicollis (Es), Erythrodiplax fusca (Ef), Ladona deplanata (Ld), Libellula luctuosa (Ll), Libellula quadrimaculata (Lq), Pachydiplax longipennis (Plo), Plathemix lydia (Ply), Sympetrum corruptum (Sc), and Tetragoneuria cynosure (Tc).