Fig. 2. Forward genetic screen with tgMOR platform identifies orphan receptor FRPR-13 as negative regulator of MOR signaling.
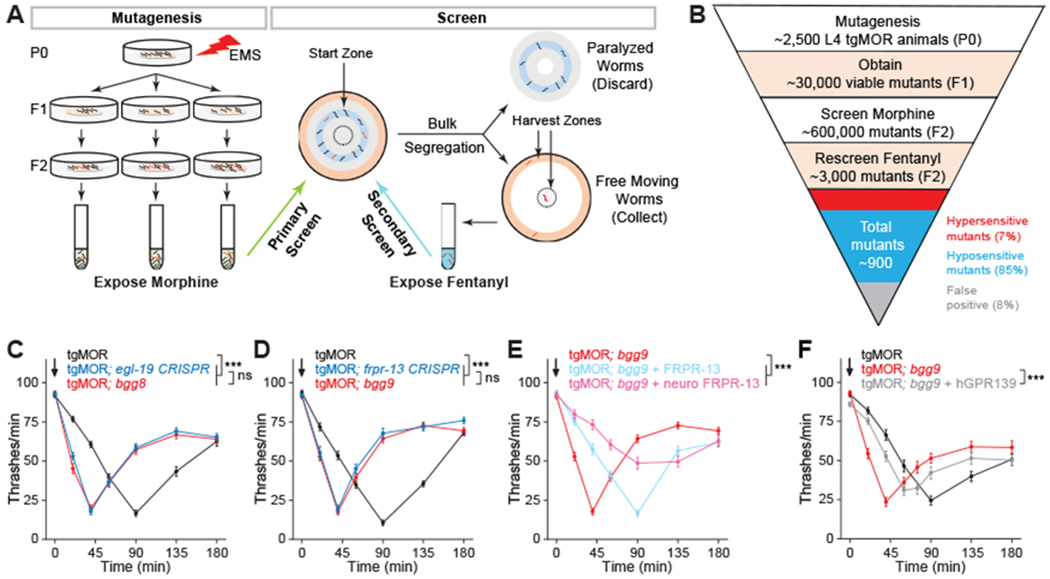
(A) Two-step genetic screen for tgMOR mutants with altered opioid sensitivity. (B) Outline of steps, generations, number of independent mutants isolated, and phenotypic categories observed for genetic screen with tgMOR. (C) tgMOR; bgg8 mutants are hypersensitive to fentanyl and CRISPR/Cas9 editing validates egl-19 as gene causing hypersensitivity. (D) tgMOR; bgg9 mutants are hypersensitive to fentanyl and CRISPR/Cas9 editing validates frpr-13 as gene causing hypersensitivity. (E) Transgenic expression of FRPR-13 using native or neuronal promoters reverses fentanyl hypersensitivity in tgMOR; bgg9 animals. (F) Transgenic expression of human GPR139 reverses fentanyl hypersensitivity in tgMOR; bgg9 animals. Arrows denote fentanyl (10μM) application. For all genotypes and drug conditions, means are shown from 30 or more animals obtained from three independent experiments. Error bars are S.E.M. Significance tested using two-way ANOVA. *** p<0.001 and ns = not significant
