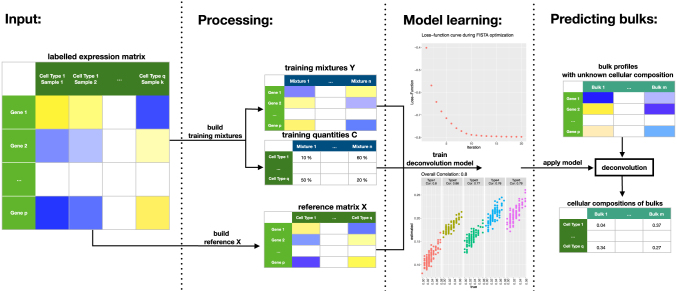
FIG. 1.
Workflow of a digital tissue deconvolution (DTD) analysis with loss-function learning. Input: an expression matrix, where each sample is labeled with its cell type. Processing: the labeled samples are used to build both a reference matrix and artificial mixtures of known cellular composition. Model learning: the algorithm iteratively searches for parameters g, which maximize the correlation between the estimated and the true cellular compositions, where the training data and the reference matrix are used. Here, functions visualize the result and assess the performance of the DTD model. Predicting bulks: the DTD model is applied to bulk gene expression data to estimate the underlying cellular composition.