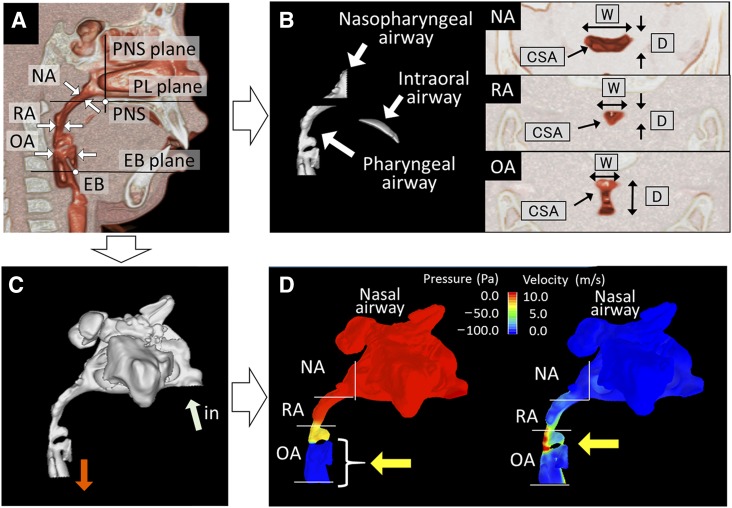
Figure 1. Measurement of the upper airway.
(A) Landmarks and planes for the axial airway section. EB = base of the epiglottis, EB plane = the plane parallel to the PL plane passing through the EB, NA = nasopharyngeal airway cross section measured at its narrowest part, OA = oropharyngeal airway cross section measured along the PL plane passing through the midpoint of the bilateral gonion, PL plane = the plane parallel to the hard palate passing through the PNS, PNS = posterior nasal spine, PNS plane = the plane perpendicular to the hard palate passing through the PNS, RA = retropalatal airway cross section measured parallel to the PL plane at the narrowest part. (B) Measurement of airway volumes and cross sections. Nasopharyngeal airway volume between the PNS and PL planes. Intraoral airway volume between the palate and the tongue. Pharyngeal airway volume between the PL and EB planes. CSA = cross-sectional area, D = depth, W = width. (C) Volume rendering and numeric simulation of the three-dimensional upper airway (light blue arrow, inlet air flow; orange arrow, outlet air flow). (D) Evaluation of the upper airway ventilation condition. Left: yellow arrow indicates area of large negative pressure suspected as the site of pharyngeal airway collapse. Right: yellow arrow indicates area of higher velocity suspected as the obstruction site.