Fig. 3 |. Benchmarking MARIA performance against existing binding-based methods with independent HLA-DR test sets.
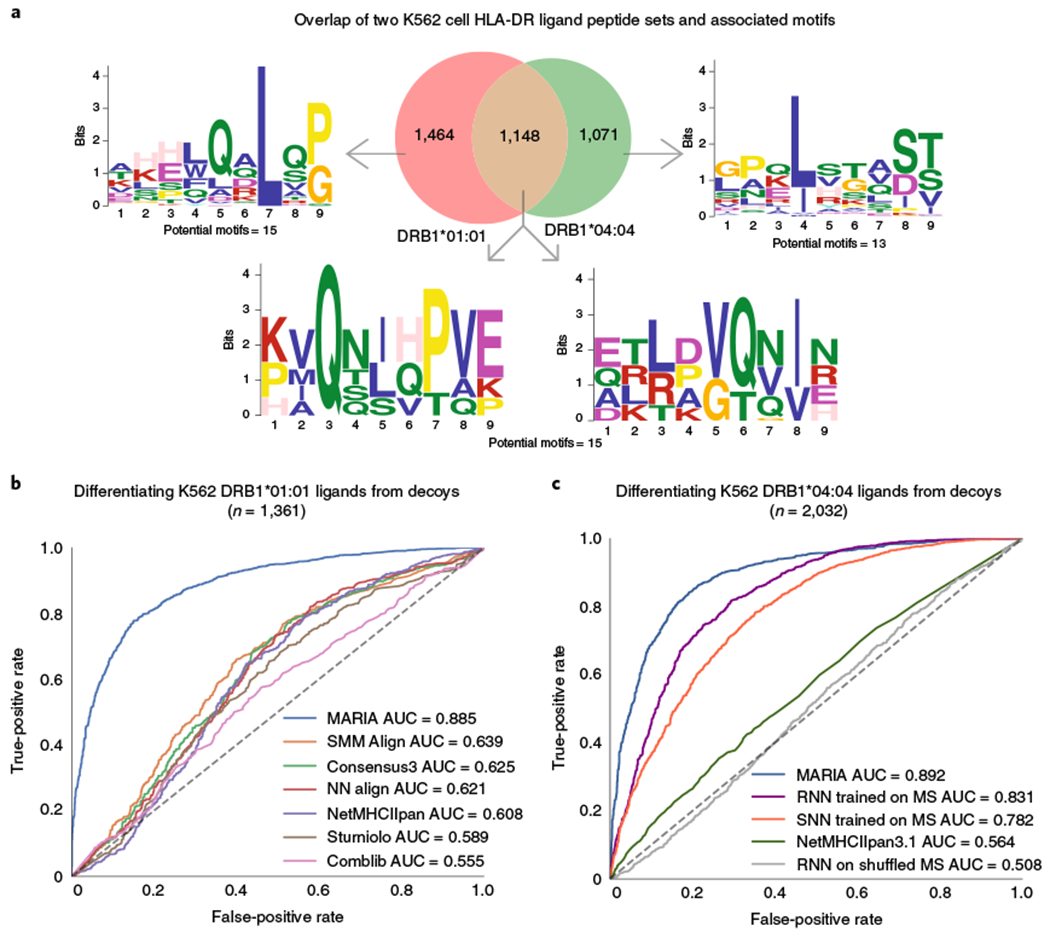
a, Overlap and sequence motifs of two HLA-DR ligand sets identified from two monoallelic K562 cell lines. A proportion (31%) of peptides appeared in both the HLA-DRB1*01:01 (n = 2,430) and HLA-DRB1*04:04 (n = 2,072) ligand sets when considering substring matches. The sequence motifs with highest statistical significance (P < 1 × 10−7, multiple hypergeometric test implemented by MEME) are shown. For full potential motifs, see Supplementary Table 4. b, Performance of MARIA and six alternative methods when differentiating 1,361 K562 HLA-DRB1*01:01 ligands from 1,361 human decoys. MARIA outperformed the second-best method (SMM Align; DeLong test, P < 1 × 10−5). Limited by the IEDB Concensus3 package, only ligand sequences ≥15 amino acids are included in this comparison. c, Performance of MARIA and four alternative methods differentiating 2,032 K562 DRB1*04:04 ligands from 2,032 human decoys. MARIA achieved an AUC of 0.89 AUC as compared to an AUC of 0.56 for NetMHCIIpan. RNN and SNN trained on MCL ligands obtained AUC values of 0.83 and 0.78, respectively.
