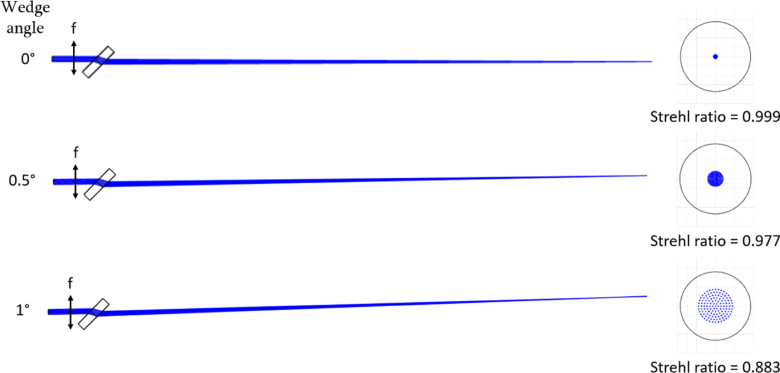
Fig. 3.
Wedge angle’s effect on aberrations of a converging beam. Schematics on the left each start with a 3.6 mm diameter incident beam of 550 nm light that transmits through a paraxial lens with f = 400 mm (corresponding to a vergence of 0.625 D if preceded by a transverse magnification of ½). Light after the lens focuses through 6 mm thick wedge plate beam splitter made of fused silica and tilted at 45°. The wedge angle is varied from 0° to 1° (from top row to bottom row) and the corresponding spot diagrams at the focal plane are shown at the right.