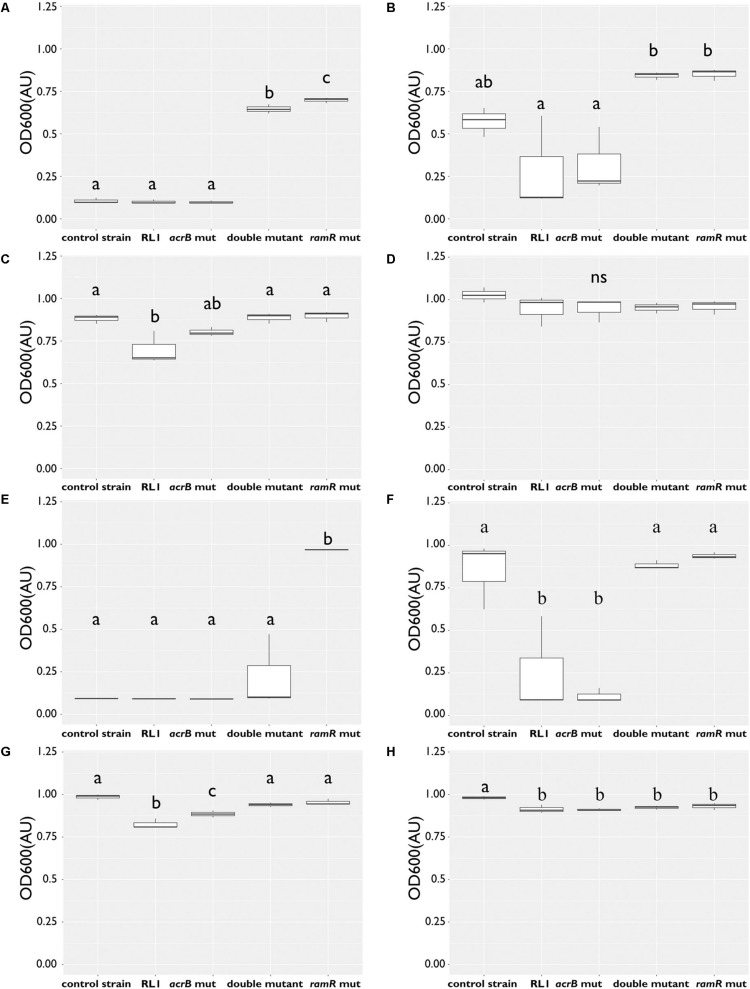
FIGURE 3.
The mutation in ramR induced hyposensitivity to chloramphenicol and ampicillin, whereas the mutation in acrB induced hypersusceptibility to ampicillin. Bacteria were grown overnight with antibiotics at 37°C to determine their minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) to chloramphenicol or ampicillin. OD600 of the control strain RL1, acrB mut, double mutant, and ramR mut was measured following 18 h. OD600 of bacteria grown with chloramphenicol at concentration of (A) 5.8 μM, (B) 2.9 μM, (C) 1.8 μM, and (D) at the absence of chloramphenicol. OD600 of bacteria grown with ampicillin at concentration of (E) 33.6 μM, (F) 16.8 μM, (G) 8.4 μM, and (H) at the absence of ampicillin. The values are average of three biological replicates; each was performed in duplicates. Statistical analysis was performed using Tukey multiple-comparisons test. Statistically significant differences are indicated as a≠b≠c, P < 0.05.