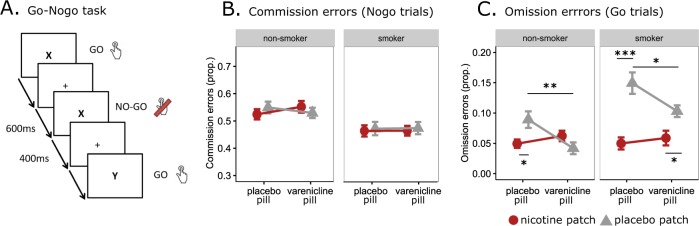
Fig. 2. Go–Nogo task.
a Trial timing of the task. Stimuli alternated between “X” and “Y” on each trial; participants were instructed to respond when the stimulus presented on the screen was different from the previously presented stimulus (Go trial) and to suppress a response when the stimulus was identical to the previously presented stimulus (No-go trial). Trials were spaced 1 s apart. Nogo trials are modeled against the implicit baseline, which consists of Go trials and fixation between trials (as in [26, 28, 60, 61]). The timing of Nogo trials is temporally jittered so that these trials can be modeled. b, c Go–Nogo performance. Error rate on Nogo (b) and Go (c) trials. Error bars indicate +/−1 standard error of the mean. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.