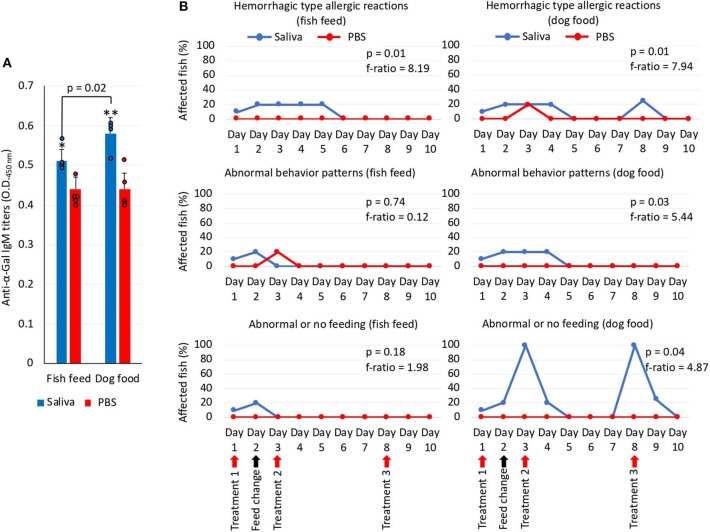
Figure 7.
Zebrafish injected with tick saliva and fed with red meat develop allergic reactions and abnormal behavior and feeding patterns (Experiment 2). (A) The IgM antibody titers against α-Gal were determined by ELISA, represented as the average ± SD OD at 450 nm and compared between fish treated with tick saliva and the PBS-treated control group and between fish fed on fish feed or dog food Student t-test (*p = 0.003, **p = 0.0008; N = 4–5 biological replicates with individual values shown). (B) Zebrafish local allergic reactions and behavior were examined immediately after treatment or feed change and followed daily until the end of the experiment at day 10. The percent of zebrafish affected by allergic reactions and abnormal behavior and feeding on each group fed with fish feed or dog food was compared between saliva-treated and PBS-treated control fish by a one-way ANOVA test (https://www.socscistatistics.com/tests/anova/default2.aspx) (p = 0.05; N = 4–5 biological replicates).