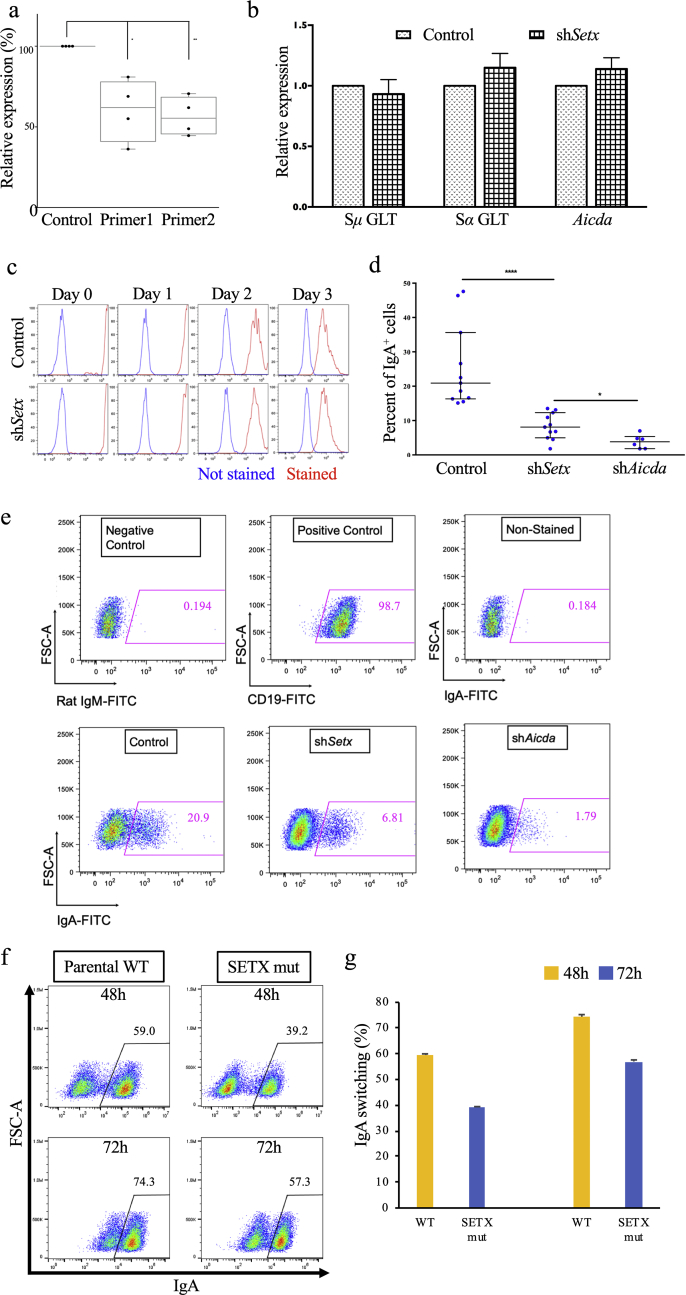
Figure 3.
SETX is important for robust CSR in CH12–F3 B cell lines. (a) Setx transcription levels in the knockdown background. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed on murine CH12–F3 cells containing a control vector or a SETX knockdown construct. Displayed here are results of an analysis using two primer sets. Results are shown relative to control vector levels. Student's t-test was used in either case, and primer pair 1 had p = 0.0061, while primer pair 2 had p = 0.0003. (b) Transcription at IgH switch sequences and Aicda in knockdown background. Sμ and Sα germ line transcripts (GLT) in a shSETX knockdown background are shown, as is the transcription at mouse Aicda, relative to control background. We observed no statistically appreciable defect in transcription at any of the three loci. (c) Proliferation of SETX knockdown CH12–F3 cells. Using the dilution dye VPD450, the proliferation of CH12–F3 cells containing control vector or the shSETX knockdown construct was tracked over 3 days. Unstained cells are shown in blue; red denotes stained cells. As the cells proliferate, the VPD450 intensity of stained cells is diluted and nears that of unstained cells. (d) Summary of multiple experiments for CSR efficiency of AID-deficient (shAID), SETX-deficient (shSETX) and vector control (control) backgrounds. CSR decrease in shSETX relative to control is statistically significant (unpaired Student's t-test, p = 0.0002), as is CSR decrease in shAID relative to shSETX (unpaired Student's t-test, p = 0.0182). (e) Representation of one experiment from (d). (f) FACS plots of IgA CSR following 48 h and 72 h of stimulation of parental CH12–F3 cells and SETX KO CH12–F3 cells, generated by the CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing approach. (g) The FACS plot shown in (f) is quantitated through three independent stimulations of the SETX knockout clones.