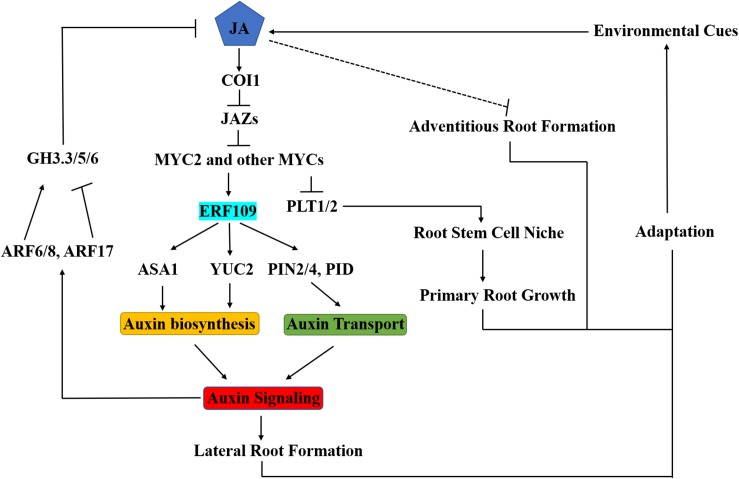
FIGURE 2.
Integration of JA into Auxin Signaling in Arabidopsis Root Development. Plants generate JA in response to environmental cues. COI1 receptor perceives JA, and then recruits JAZs subjected to degradation. Subsequently, MYC2 can activate transcription of early JA-responsive genes. JA promotes lateral root formation by regulating auxin biosynthesis (via ASA1 and YUC2) and transport (via PID and PIN2/4). Transcription factor ERF109 functions as a key crosstalk node in this process. JA inhibits primary root development by repressing the expression of PLT1 and PLT2. Auxin modulates JA homeostasis by regulating GH3.3/5/6 through ARF6/8/17, then influences adventitious root formation. Therefore, the ERF109 regulatory module plays critical roles in the growth and development of lateral, primary and adventitious roots in the adaptive response of the root system to environmental factors.