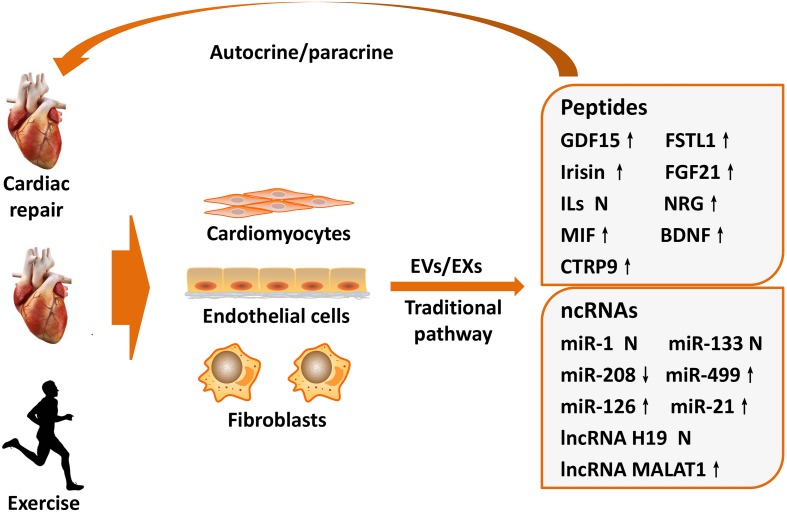
FIGURE 1.
Exercise-induced cardioprotective factors on cardiac repair after MI. The heart is an endocrine organ that produces and releases cardioprotective factors during exercise training. Cardioprotective factors mainly derived from cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and cardiac fibroblasts, which not only secreted by traditional signaling pathways but also delivered via EVs/EXs that changed components during exercise. Subsequently, these factors exert important regulatory functions for cardiac repair after MI in autocrine or paracrine manners, which may partially explain exercise-induced beneficial mechanism of MI. BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CTRP9, C1q/TNF-related protein 9; EVs, extracellular vesicles; EXs, exosomes; FSTL1, follistatin-like 1; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; GDF15, growth differentiation factor 15; ILs, interleukins; lncRNA, long non-coding RNA; MI, myocardial infarction; MIF, migration inhibitory factor; miR, microRNA; MALAT1, metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; NRG, neuregulin; ncRNAs, non-coding RNAs. ↑ means upregulate, ↓ means downregulate, N means not clarified or controversial.