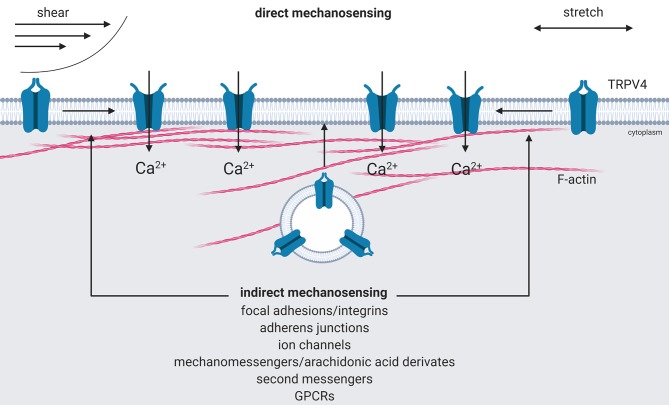
Figure 1.
Activation of mechanoTRPV4. Direct activation of TRPV4 by shear or stretch forces results in an expansion in cross sectional area that creates a tension-dependent energy difference and leads to conformational changes of the channel by force activation (direct mechanosensing). Indirect activation is mediated by intracellular signaling cascades triggered via mechanosensitive focal adhesions or adherens junctions, ion channels, by intracellular mechano- or second messengers, G-protein-coupled receptors, e.g., protease-activated receptors that either activate TRPV4 or recruit it from intracellular pools to the plasma membrane (indirect mechanosensing). Created with BioRender.com.