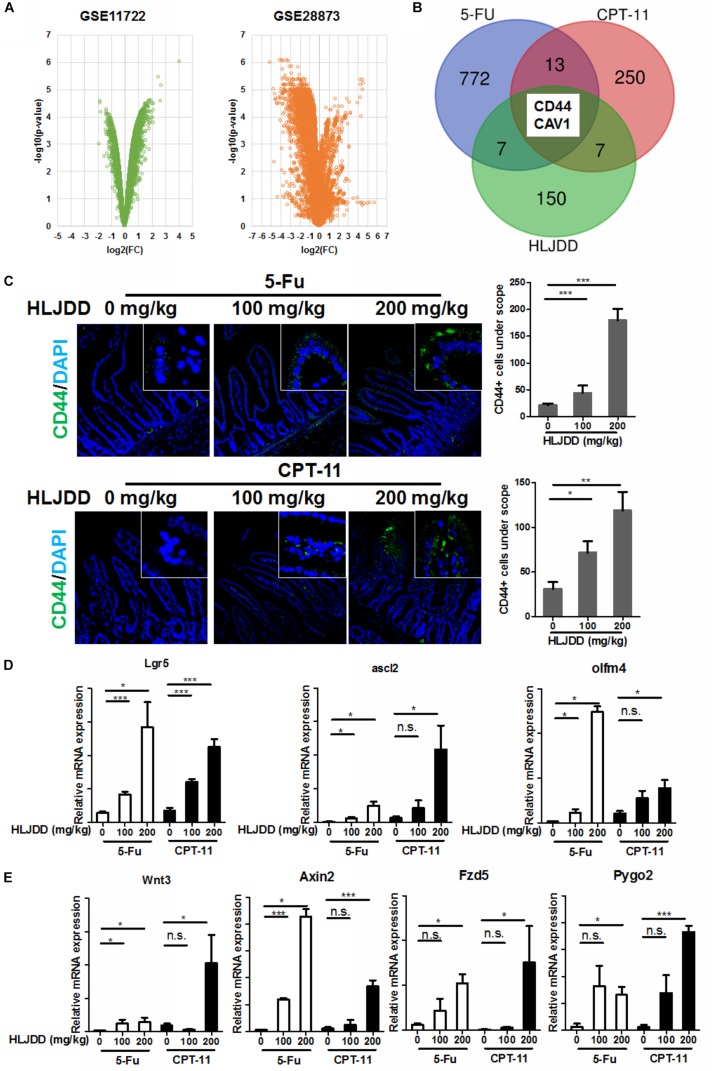
FIGURE 5.
Pre-treatment induced CD44 expression and activation of its downstream Wnt signaling in the intestinal cell of chemotherapy-treated mice. (A) showed the volcano plots of gene expression in the intestine challenged by 5-Fu (GSE28873) and CPT-11 (GSE11722). Genes with relative expression of log2(fold change) > 1 and log10(p-value) > 2 were shortlisted; (B) showed overlapped of genes with significant expression change after 5-Fu and CPT-11 treatment, and genes with expression affected by compounds in HLJDD. Tow genes, CD44 and CAV1, were the common genes among the three populations; (C) showed that pre-treatment of HLJDD could significantly improve the CD44 expression in the intestinal section of chemotherapy-treated mice; (D) showed that expression of stemness-related gene, including lgr5, ascl2 and oflm4 in the intestine cells in the intestine of chemotherapy-treated mice was induced by pre-treatment of HLJDD; (E) showed that expression of Wnt pathway-related genes, including Wnt3, Axin2, Fzd5 and Pygo2, in the intestine cells in the intestine of chemotherapy-treated mice was induced by pre-treatment of HLJDD; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when compared with the model group.