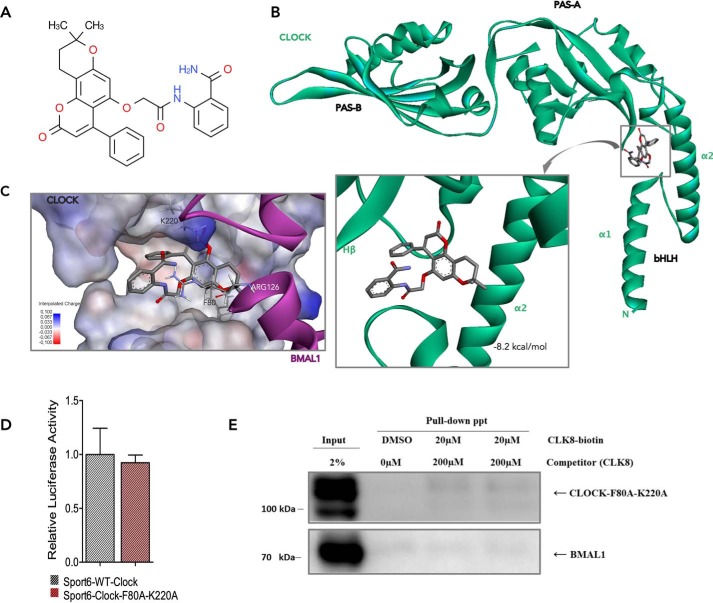
Figure 3.
Docking of CLK8 into the CLOCK-binding site. A, chemical structure of CLK8. B, best binding mode of CLK8 to CLOCK (green) with a predicted binding energy of −8.2 kcal/mol. CLK8 can enter the hollow between the α2 helix of the bHLH domain and the Hβ strand of the PAS-A domain of CLOCK. C, superposition of CLK8 and Arg-126 of BMAL1 (magenta). CLK8 and Arg-126 of BMAL1 share the same binding region in the CLOCK structure, where Phe-80 plays an essential role. The positively charged Lys-220 in the PAS-A domain of CLOCK also contributes to a π-cation interaction with CLK8. D, comparison of WT CLOCK and mutant CLOCK-F80A,K220A. The transcriptional functions of WT and mutant CLOCK were compared by a Per1-Luc assay in HEK293T cells. Data are mean ± S.E.; n = 3 independent experiments. E, pulldown assay using whole cell lysate of HEK293T cells overexpressing CLOCK-F80A,K220A and BMAL1.