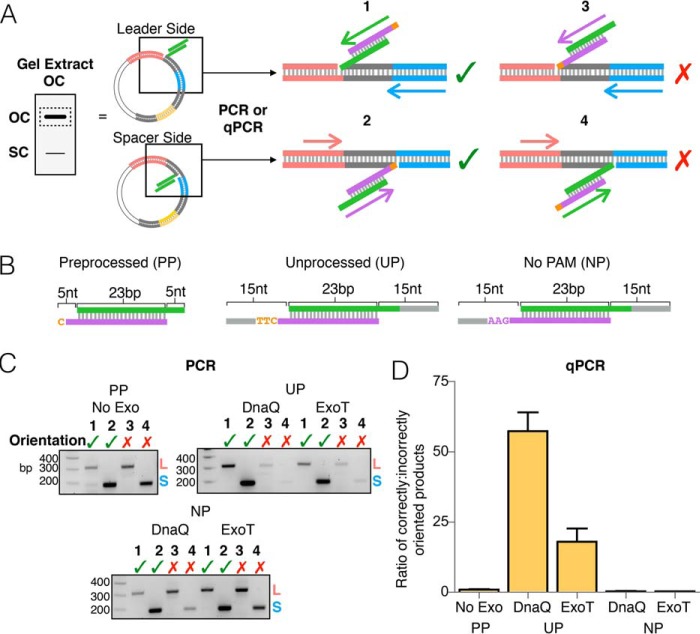
Figure 2.
Orientation bias displayed by DnaQ- and ExoT-mediated integration. A, schematic depicting PCR amplification of half-site integration events. Products of integration reactions (open circle plasmid) were gel-extracted and used as templates in four different PCRs, using different primer sets to identify the site of integration and the orientation of integrated spacer. Numbers above schematics indicate the four possible integration events. A green checkmark indicates a half-site product in the correct orientation; a red X indicates a product in the incorrect orientation. B, substrates used in the integration reactions. C, agarose gels of all end-point PCRs. Prespacer (processed prespacer (PP), unprocessed prespacer (UP), or no PAM prespacer (NP)) and exonuclease used in the integration reactions are shown above each gel. Numbers refer to the four reactions in A. D, graph depicting the ratio of correctly oriented to incorrectly oriented half-site products determined by qPCR. Ratios represent the combined number of leader- and spacer-side integration events for each orientation, normalized to picogram amounts of the β-lactamase gene. The average of three replicates is shown with error bars representing S.D.