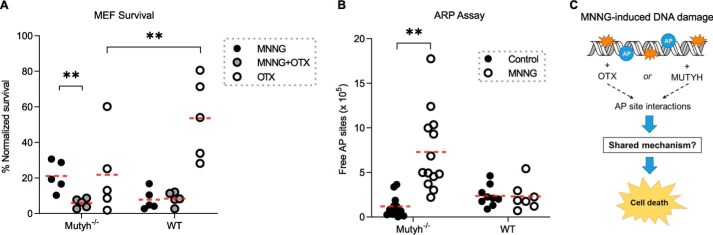
Figure 5.
Evidence of AP site interactions in MUTYH-mediated MNNG toxicity. A, cell survival data of WT and Mutyh−/− MEFs treated with 33 μm MNNG with and without 3 mm OTX or with OTX alone. The enhanced survival of Mutyh−/− MEFs to MNNG is abolished by OTX (1st column versus 2nd column, p = 0.005) but has no effect on WT MEFs (4th column versus 5th column). OTX alone is significantly more toxic to Mutyh−/− versus WT MEFs (3rd column versus 6th column, p = 0.011). B, ARP assay quantification of AP sites in genomic DNA extracted from MEFs treated with MNNG versus untreated control. There was a significant increase in reactive AP sites in Mutyh−/− MEFs (1st column versus 2nd column) but not in WT MEFs upon MNNG treatment (p < 0.001, t test). C, diagram summarizing experimental results, which highlights the lack of an additive effect between the small molecule OTX and MUTYH, suggesting they potentiate MNNG cell death by a similar mechanism.