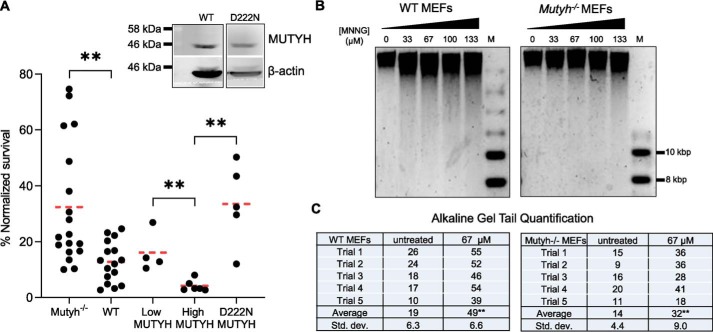
Figure 9.
MNNG-dependent cytotoxicity depends on MUTYH catalytic residue Asp-222 and leads to genomic DNA strand breaks. A, survival to low MNNG (67 μm) in Mutyh−/− MEF stable cell lines expressing recombinant D222N (5th column) versus WT MUTYH (4th column). Data from Fig. 2A are represented in the 1st to 4th columns. Inset: Western blotting of WT MUTYH expression from Fig. 2B versus D222N stable cell line MUTYH expression. There is significantly higher survival in cells expressing D222N versus WT MUTYH (4th column versus 5th column, **, p < 0.005, t test, significant with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons). B, MUTYH increases genomic strand breaks in MNNG-treated MEFs as quantified by alkaline gel electrophoresis. Genomic DNA was extracted 40 min after MNNG treatment, quantified, incubated in an alkaline loading buffer, and run on a 0.8% agarose gel overnight at pH 12.4 as detailed under “Experimental procedures.” M = molecular weight marker. C, quantification of total sample band density in the lower region (tail) versus the upper band from two biological replicates (five gels). WT cells had significantly more DNA in the lower region at 67 μm versus Mutyh−/− cells (**, t test, p < 0.01), indicative of increased strand breaks in WT versus Mutyh−/− MEFs. Trial 5 is shown, and all other gels and data are shown in Fig. S5.