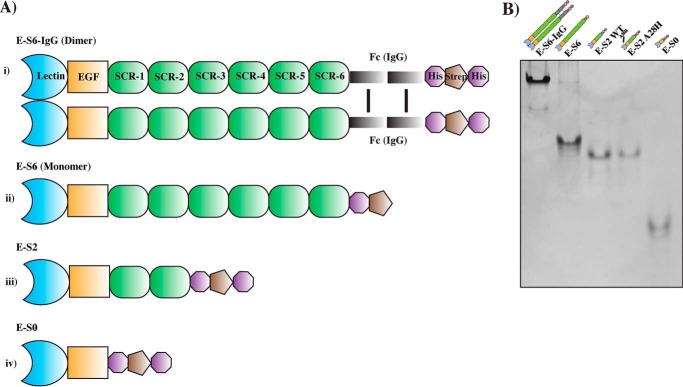
Figure 1.
Expression and purification of functional E-selectin proteins. A, schematic representation of E-selectin constructs. i, E-S6-IgG consisting of the structural domains of a commonly used E-selectin-IgG/Fc (dimer) chimera recombinant protein. ii, monomeric version of full-length E-selectin (E-S6). iii and iv, truncated E-selectin formed by domain deletion of either the last four SCRs, producing constructs with only the first two SCRs (E-S2), or deletion of all of the SCRs, yielding a minimal construct possessing only the main domains for binding (E-S0). Several tags were included at the C terminus of each construct, such as a histidine tag (double His6 or a single His8) and a Strep-tag, to facilitate the purification and subsequent immobilization of E-selectins (note that an Avi tag located after the EGF domain in E-S6-IgG, E-S2, and E-S0 and a TEV tag included before His8 in E-S6 are omitted from this diagram as they were not addressed in this study). B, analytical native PAGE of the recombinant E-selectin proteins. E-S6-IgG, E-S6, E-S2, E-S2-A28H, and E-S0 were diluted in 1× Native PAGE buffer, loaded on a 10% TBE gel and run in 1× Tris-glycine buffer. The majority of molecules in each recombinant protein sample appear as a single species, with a minor amount of oligomerization in case of E-S6; the majority of molecules in E-S6-IgG appear as a dimer through the C terminus Fc region, with some slightly monomeric versions appearing as a faint band of lower molecular weight.