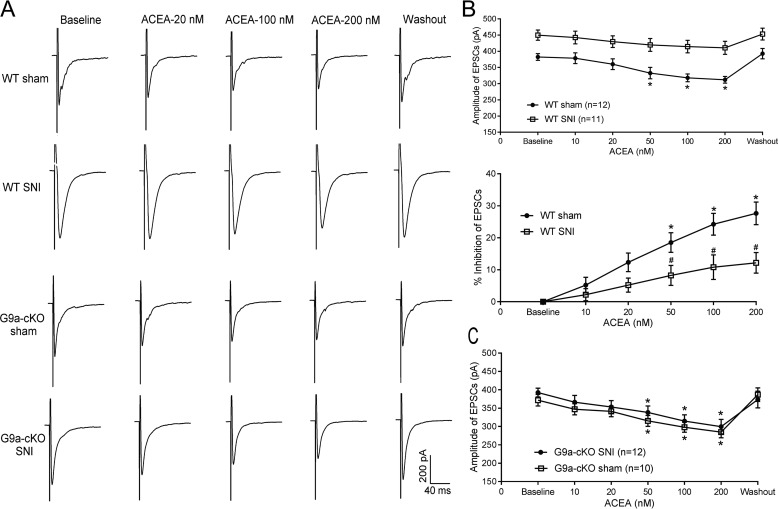
Figure 7.
Genetic ablation of Ehmt2 in DRG neurons restores the inhibitory effect of the CB1R agonist on glutamate release from primary afferent terminals diminished by nerve injury. A–C, representative recording traces and mean data showing the inhibitory effect of 10–200 nm ACEA on the amplitude of EPSCs of dorsal horn neurons evoked monosynaptically from dorsal root stimulation in WT (A and B) and Ehmt2-cKO (A and C) mice subjected to sham or SNI surgery. In the top panel of B, the baseline amplitude of EPSCs was different between the sham and SNI groups, and the effect of ACEA was normalized to the respective baseline amplitude (percent inhibition) for comparison in the bottom panel. The number of neurons tested in each group is indicated in B and C. Data are shown as means ± S.E. *, p < 0.05 compared with the respective baseline value. #, p < 0.05 compared with the WT sham group at the same ACEA concentration (two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test).