FIG 2.
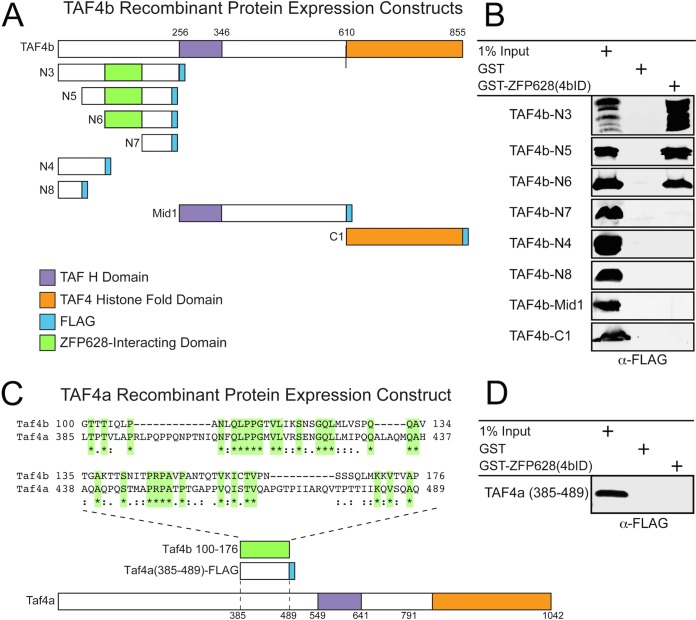
A discrete portion of the TAF4b coactivator domain is required for its direct interaction with ZFP628. (A) A graphic representation of each TAF4b recombinant protein expression construct containing a C-terminal FLAG epitope, as well as their corresponding TAF H and histone fold domains. The ZFP628-interacting domain identified in Fig. 1 is indicated. The location of each domain is representative of its position within each protein. (B) Defining an interaction domain within TAF4b required for a direct protein-protein interaction with ZFP628. Bacterial soluble protein extracts containing different portions of TAF4b (N3 to N8, Mid1, and C1) were incubated with immobilized GST or GST-ZFP628, and bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG antibodies. (C) Protein sequence comparisons between mouse TAF4b and TAF4a identified a small domain of TAF4a (amino acids 385 to 389) that displayed limited conservation to the ZFP628-interacting domain of TAF4b. Amino acid identities between these two domains are highlighted in green and indicated by an asterisk, and amino acid conservation is indicated by single and double dots. (D) Bacterial soluble protein extracts containing this domain of TAF4a fused to a C-terminal FLAG epitope were incubated with immobilized GST or GST-ZFP628, and bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG antibodies.