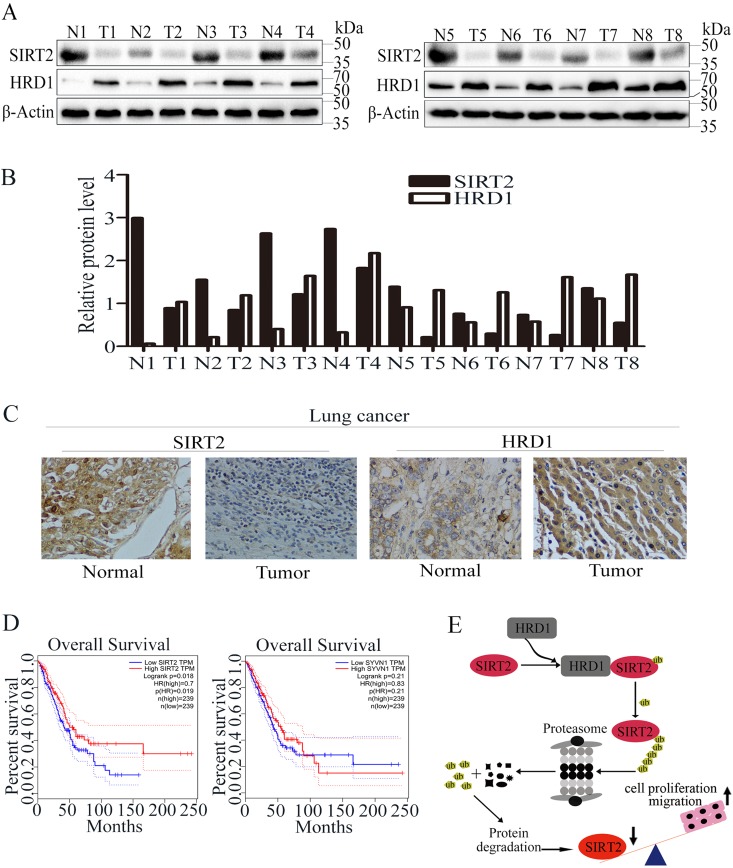
FIG 7.
HRD1 and SIRT2 expression in lung cancer. (A) The protein levels of HRD1 and SIRT2 were measured in lung cancer tissue specimens (T; n = 8) and matched with adjacent normal tissues (N; n = 8) through Western blotting. (B) The relative HRD1 and SIRT2 protein levels in normal and cancer tissues were quantified. (C) Representative images showing the immunohistochemical staining of HRD1 and SIRT2 in normal and lung cancer tissues. (D) Analysis of the GEPIA data indicates a significant positive correlation of SIRT2 expression and a negative correlation of HRD1 expression between their expression and the overall survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients. GEPIA uses the log rank test, also known as the Mantel-Cox test, for the hypothesis test. The Cox proportional hazard ratio and the 95% confidence interval information are also included in the survival plot. (E) Schematic model of SIRT2 regulation by HRD1. Upregulation of HRD1 in lung cancer patients leads to downregulation of SIRT2, thus resulting in enhanced cell proliferation and lung tumorigenesis.