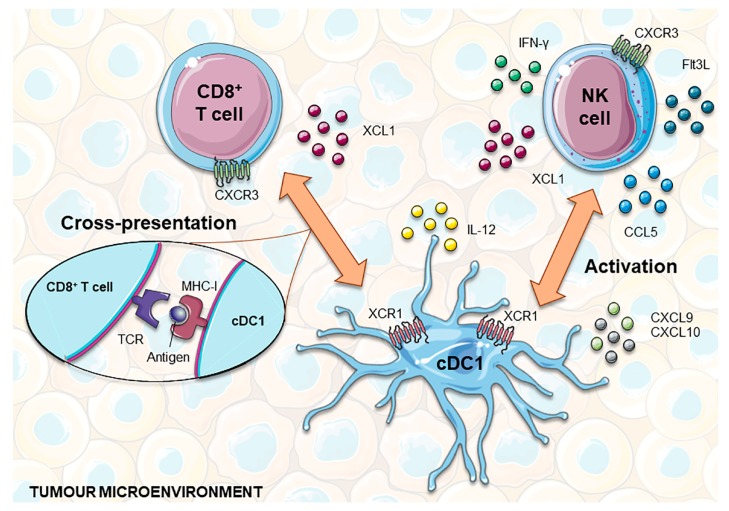
Figure 2.
cDC1 interplay with CD8+ T and NK cells to develop anti-tumor responses. NK and CD8+ T cells express XCL1, which attracts XCR1+ cDC1 into the tumor microenvironment. In addition, NK cells can also produce CCL5, helping to recruit this subset of DCs. In turn, cDC1 are the main source of the chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10, chemoattractants for T and NK cells. Functionally, cDC1 are highly capable of cross-presenting tumor antigens via MHC-I to CD8+ T cells and producing IL-12, which promotes T cell cytotoxicity and the production of INF-γ by NK cells. Furthermore, NK cells produce Flt3L that holds up the viability and functional capacities of cDC1 within the tumor microenvironment and can also promote their local differentiation from recruited precursors. cDC1, classical dendritic cell 1; Flt3L, FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; MHC-I, major histocompatibility complex I; NK, natural killer; TCR, T cell receptor; XCL1, X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 1.