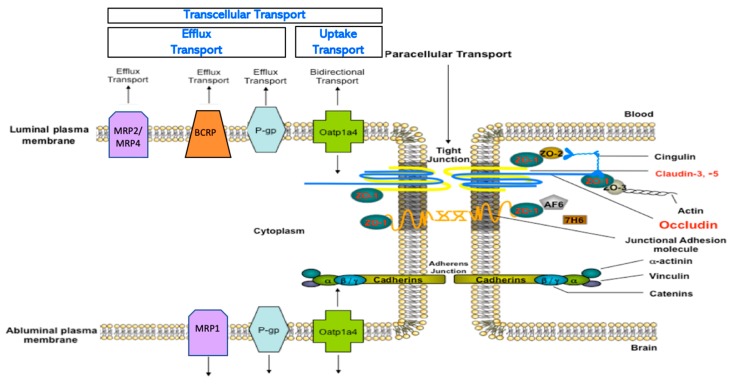
Figure 2.
Physical and biochemical characteristics of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Physiologically, paracellular diffusion is restricted by tight junction protein complexes and adherens junctions. Transporters contribute to biochemical barrier properties. Specifically, efflux transporters such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp), Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP), and Multidrug Resistance Proteins (MRPs) limit the ability of drugs to permeate the BBB and accumulate in brain parenchyma. The BBB also possesses uptake transporters such as organic anion transporters in humans/rodents (OATPs/Oatps), which can facilitate selective uptake of therapeutics into the brain. While organic cation transporters (OCTs) have also been detected at the BBB, their exact localization in brain microvascular endothelial cells is unknown.