Figure 1. H2AX-Y142 is an essential amino residue for completing spermatogenesis.
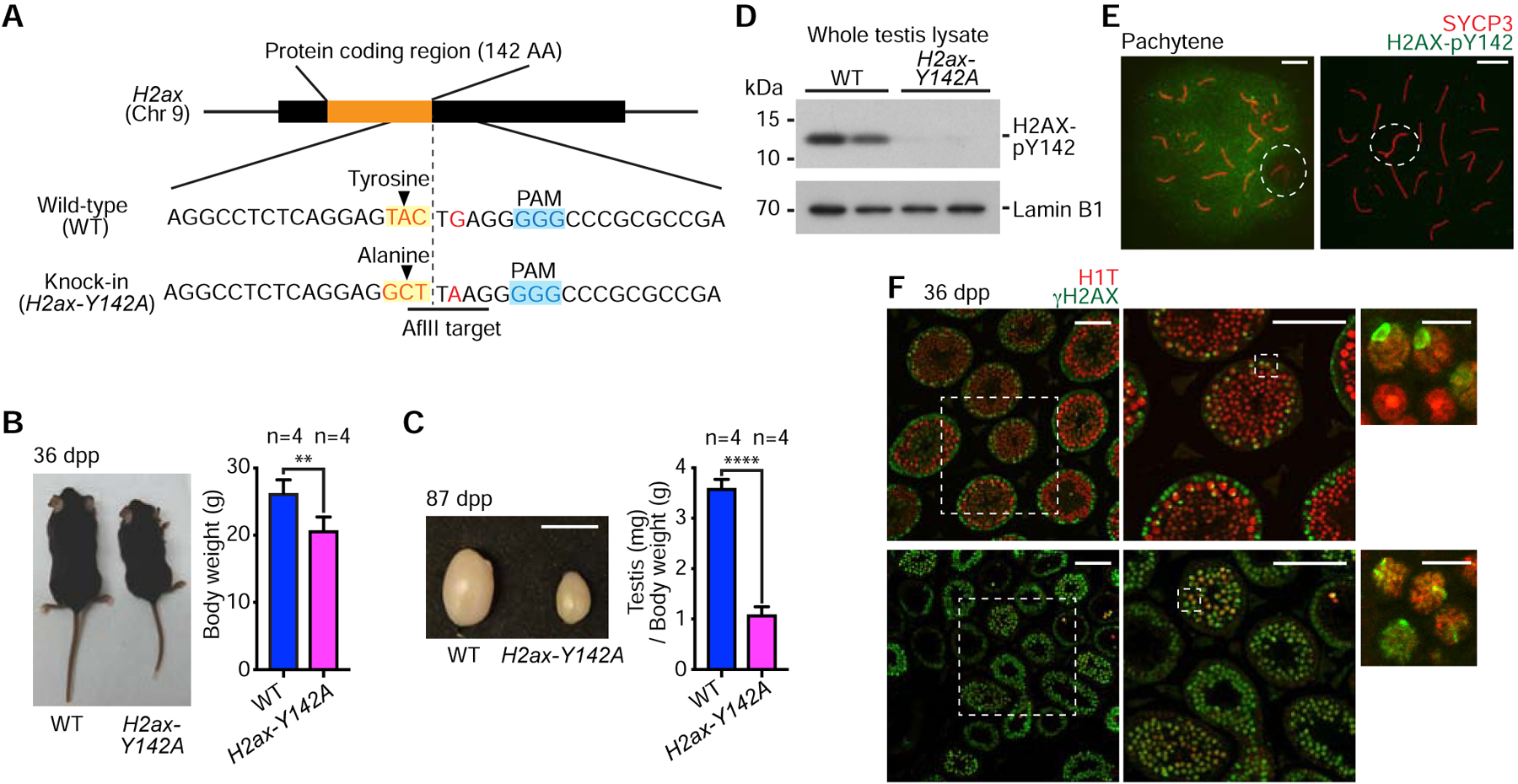
(A) Schematic: Induction of a point mutation and resulting sequence alteration. The introduction of an AflII target site was used to screen mutant mice.
(B) Wild-type (WT) and H2ax-Y142A mice at 36 days post-partum (dpp). Body weights are shown as mean ± s.e.m. from 4 independent pairs of WT and H2ax-Y142A mice. ** p < 0.01, unpaired t test.
(C) Testes from WT and H2ax-Y142A mice at 87 dpp. Scale bar: 1 cm. Ratios of testis weight (mg) to body weight (g) shown as mean ± s.e.m. for 4 independent pairs of WT and H2ax-H142A mice. **** p < 0.0001, unpaired t test.
(D) Western blot of WT and H2ax-Y142A lysates from whole mouse testes with anti-H2AX-pY142 antibody. 20 μg protein samples were loaded in each lane. Two independent samples for WT and H2ax-Y142A are shown. Loading control: Lamin B1.
(E) Chromosome spreads of WT and H2ax-Y142A pachytene spermatocytes immunostained with antibodies raised against SYCP3 and H2AX-pY142. Dashed circles indicate the sex chromosomes. Scale bars: 10 μm.
(F) Testis sections from WT and H2ax-Y142A mice immunostained with antibodies raised against H1T and γH2AX. Dashed squares are magnified in panels to the right. White arrowheads indicate γH2AX signals on sex chromosomes in mid pachytene (H1T-positive) spermatocytes. Scale bars in larger panels: 100 μm; scale bars in smaller panels: 10 μm.
See also Figure S1.
