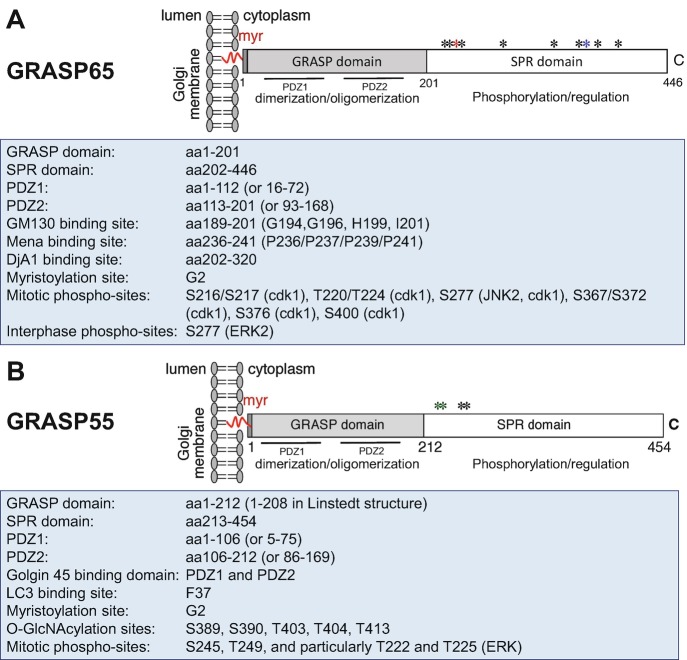
Fig. 19.1.
Structure, modification, and binding sites on GRASP65 (a) and GRASP55 (b). Rat GRASP65 and GRASP55 sequences are used for illustration. Both GRASPs share a similar structure: a conserved N-terminal GRASP domain consisting of two PDZ domains (PDZ1 and PDZ2) and a C-terminal Serine/Proline-Rich (SPR) domain with multiple phosphorylation sites (indicated by asterisks) that are involved in GRASP modulation during the cell cycle. Both GRASP65 and GRASP55 are peripheral membrane proteins attached to the Golgi membranes via N-terminal myristoylation and the interaction with their membrane-bound partner proteins (GM130 and Golgin-45, respectively). GRASP65-binding proteins Mena and DjA1 have been identified to enhance Golgi ribbon linking and stacking, respectively. GRASP55 is regulated by O-GlcNAcylation depending on the glucose level and interacts with LC3 and LAMP2 to facilitate glucose starvation-induced autophagy