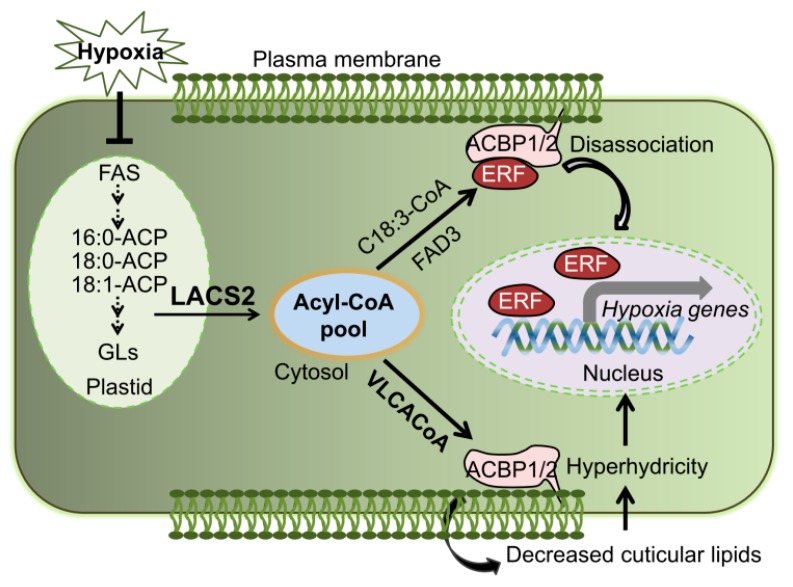
Figure 6.
Model of the role of LACS2 in plant responses to hypoxia stress. Lipid remodeling is vitally necessary for hypoxic tolerance in plant [7,8,18,35]. By inactivation of fatty acid synthetase (FAS) and accelerating the fatty acid degradation, submergence-induced hypoxia decreases the fatty acid levels. LACS2 is essential for plant hypoxic tolerance and acyl-CoA metabolism during hypoxia. Specifically, the hypoxia-induced 18:3-CoA catalyzed by LACS2 and FAD3, interacts with ACBP1 or ACBP2, leads to the dissociation of the ACBPs–ERF-VII complex and subsequently activates the signaling cascades of ACBPs–ERF-VII. On the other hand, VLCACoAs produced by LACS2 are shuttled by ACBP1 or ACBP2 to facilitate the biosynthesis of cuticular lipids, which may contribute to plant surface permeability, cellular hyperhydrivity, and gas exchange under submergence conditions. ACBP; acyl-CoA-binding protein; ACP, acyl carrier protein; ERF, ethylene response factor; FAS, fatty acid synthase; VLCACoA, very-long-chain acyl-CoA.