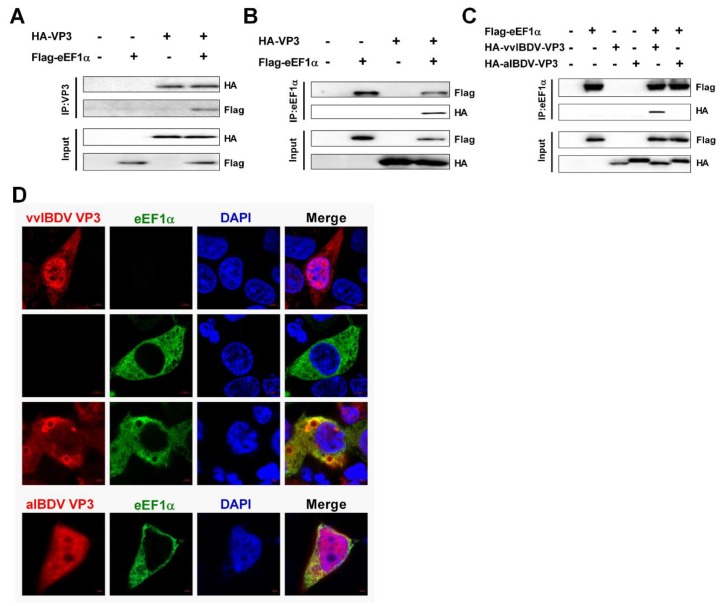
Figure 3.
cheEF1α interacts with vvIBDV VP3, but not aIBDV. VP3 (A) 293T cells were transfected with HA-vvIBDV VP3 and Flag-cheEF1α expression plasmids. Cell lysates were prepared at 36 h post transfection and immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody and immunoblotted with anti-Flag or anti-HA antibodies. (B) 293T cells were transfected as in (A). Cell lysates were prepared at 36 hours post transfection and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotted with anti-Flag or anti-HA antibodies. (C) 293T cells were transfected with HA-vvIBDV VP3 and Flag-cheEF1α or HA-aIBDV VP3 and Flag-cheEF1α expression plasmids. Cell lysates were prepared at 36 h post transfection and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotted with anti-Flag or anti-HA antibodies. (D) 293T cells were transfected with HA-vvIBDV VP3 and/or Flag-cheEF1α for 36 h and then fixed and processed for dual-immunostaining. Cell nuclei were counterstained with 4′6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). VP3 (red) and cheEF1α (green) proteins were visualized by labelling with anti-HA and/or anti-Flag antibodies, respectively, and were observed using confocal microscopy. Scale bars were marked down right corner. VP3 staining is shown in red, and cheEF1α staining is shown in green; merged images are shown with areas of co-localization in yellow. Each co-immunoprecipitation experiment was repeated three times.