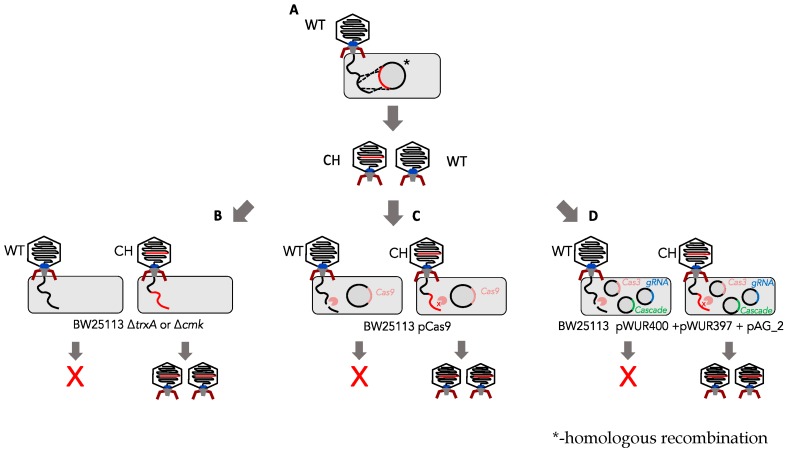
Figure 1.
Summary of marker-based vs. marker-less selection methods. (A) The homologous recombination step allows for generation of a mixed population of chimeric/mutant (CH) and wild-type (WT) phages. (B) Marker-based selection requires a gene encoding an essential host factor to be incorporated into the region that will homologously recombine in step A. Mutants are then selected for on E. coli cells that are deficient in this host factor. For phage T7 either E.coli ΔtrxA or E.coli Δcmk can be used for positive selection. (C) Type II CRISPR system consists of one vector (pCas9: contains Cas9 as well as direct repeat regions and guide RNA). (D) A Type I CRISPR system consists of three vectors (pWUR400:Cas3, pWUR397:cascade system and pAG_2:guide RNA). Both CRISPR systems target wild-type phage, enriching for mutants.