Figure 6.
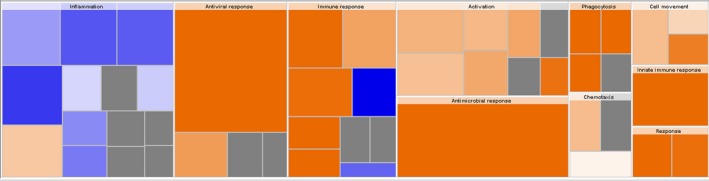
The biological function analysis of IPA. Results show that there are total of 10 main functional modules were associated with the differentially expressed genes. The names of these 10 modules are inflammation, antiviral response, immune response, activation, antimicrobial response, phagocytosis, chemotaxis, cell movement, innate immune response and response. Among all the subdivision function modules of these 10 main function modules, the relevant functions that are significantly activated are phagocytosis of cells (P‐value = 1.05E‐03, z‐score = 2.941), immune response of macrophages (P‐value = 5.59E‐05, z‐score = 2.621), antiviral response (P‐value = 2.96E‐35, z‐score = 2.411) and innate immune response (P‐value = 2.40E‐11, z‐score = 2.157). The obvious inhibitory functions are immune response of brain (P‐value = 5.06E‐05, z‐score = −2.399) and encephalitis (P‐value = 1.89E‐04, z‐score = −2.212). The biological function analysis shows the enrichment of differential genes in biological function classification, ranking from high to low according to the ‐log (P‐value) value (ie ranking from small to large according to the P‐value), and the heat map of biological function shows that the up‐regulated expression of differential genes is related to the activation or inhibition of biological function. Orange means z‐score > 0, blue means z‐score < 0, and grey means no z‐score; Z‐score > 2 means that the function is significantly activated, and z‐score < −2 means that the function is significantly inhibited
