Figure 1.
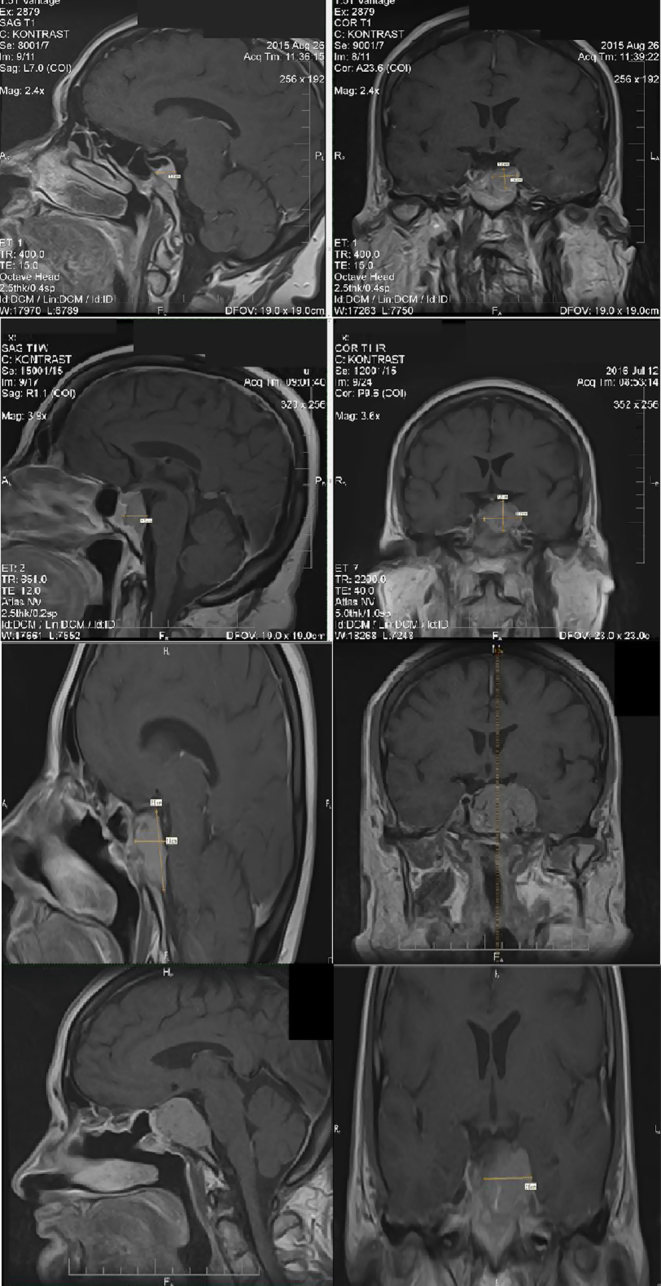
(A) 2015, MRI of the pituitary gland on T1-weighted image demonstrated a hypointense mass measuring approximately 17 × 10 × 15 mm (AP × LR × HF) and left cavernous sinus invasion. It was regarded as meningioma due to its uniform enhancement after the administration of an intravenous gadolinium contrast agent; (B) 2016, MRI of the pituitary gland on T1-weighted image demonstrated a hypointense mass measuring approximately 21 × 25 × 28 mm (AP × LR × HF) and left cavernous sinus invasion. It was regarded as meningioma due to its uniform enhancement after the administration of an intravenous gadolinium contrast agent; (C) May 2017, MRI of the pituitary gland on T1-weighted image demonstrated a hypointense mass measuring approximately 27 × 15 × 25 mm (AP × LR × HF) mostly in the sellar and suprasellar region; (D) 2018, MRI, the large enhancing mass (36 × 34 × 24 mm) was based over the sphenoid bone with its cavernous sinus invasion, lateral displacement of infundibulum, and surrounding the right internal carotid artery without obstruction.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a