Figure 2.
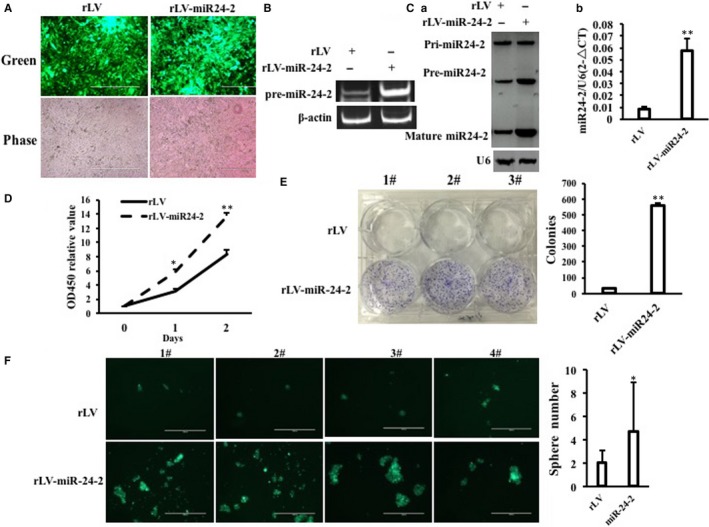
miR24‐2 accelerates growth of liver cancer cells in vitro. A, Green protein is observed under a fluorescence microscope in the two stable Hep3B cell lines by infecting with rLV or rLV–miR24‐2, respectively (original magnification ×100, scale bars, 400 μm). B, The RT‐PCR analysis for pre‐miR24‐2 in the two stable Hep3B cell lines by infecting with rLV or rLV–miR24‐2, respectively. β‐Actin as internal control. C, a, The Northern‐Western blot analysis for miR24‐2 in the two stable Hep3B cell lines by infecting with rLV or rLV–miR24‐2, respectively. U6 as internal control. b, The real‐time RT‐PCR analysis for mature miR24‐2 in the two stable Hep3B cell lines by infecting with rLV or rLV–miR24‐2, respectively. U6 as internal control. Each value was presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (Student's t test). Bar ± SEM. **P < .01; *P < .05. D, Cell proliferation assay. E, Colony formation assay. F, Cell sphere formation assay. Each value was presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (Student's t test). Bar ± SEM. **P < .01; *P < .05
