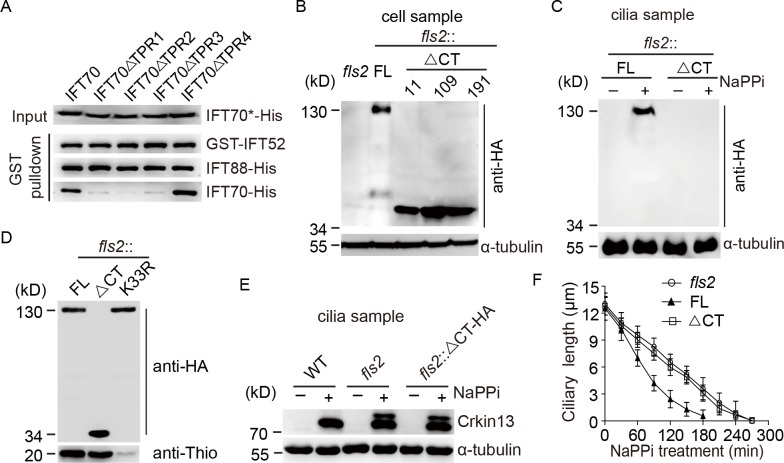
Fig 7. The C-terminal non-kinase region of FLS2 is required for its ciliary transport and proper ciliary disassembly.
(A) Deletion of TPR1, TPR2 or TPR3 of IFT70 abrogates its interaction with IFT52-IFT88 dimer. Cell lysates from bacterial cells expressing His-tagged full-length IFT70 and its various deletion mutants (IFT70*-His) were mixed, respectively, with cell lysates from cells expressing GST-IFT52 and IFT88-His followed by GST pull-down assay. His and GST antibodies were used for immunoblotting. (B) Expression of C-terminal deletion mutant of FLS2 in fls2 cells. fls2 cells expressing HA-tagged full-length (FL) FLS2 or its C-terminal deletion mutants (ΔCT) (three strains 11, 109, 191) were analyzed by immunoblotting. fls2 cells were used as a negative control. (C) The C-terminal region of FLS2 is required for its ciliary transport. Cilia were isolated from fls2 cells expressing full-length FLS2 or ΔCT mutant that were treated with or without NaPPi for 10 min followed by immunoblot analysis. (D) The C-terminal region of FLS2 does not affect its kinase activity. FLS2 was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA from cell samples as indicated and subjected to immunoblot analysis and in vitro kinase assay. In vitro kinase assay was performed as shown in Fig 3C. (E-F) Failed ciliary transport of FLS2 by C-terminal deletion induces CrKinesin13 phosphorylation and impairs ciliary disassembly. Cilia isolated from cell samples as indicated were analyzed by immunoblotting (E). fls2 cells expressing full-length (FL) FLS2 or ΔCT mutant were induced for ciliary disassembly by NaPPi treatment followed by ciliary length measurement at the indicated times. fls2 cells were used as control. Bars indicate SD.