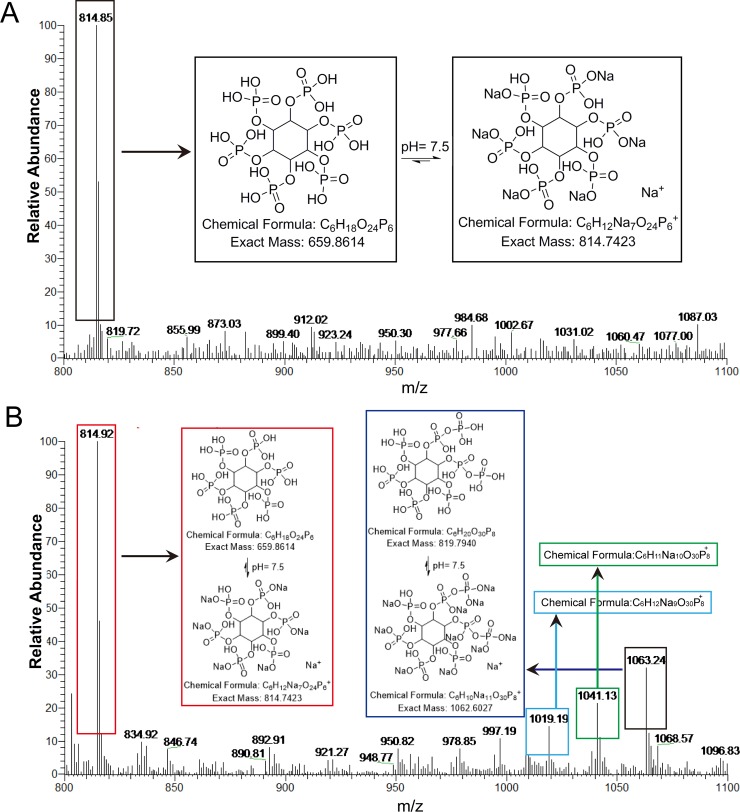
Fig 6. Identification of 5,6[PP]2-InsP4 and InsP6 by HPLC-MS.
(A) The InsP6 standard (phytic acid sodium salt hydrate, C6H18O24P6·xNa+·yH2O) was analyzed by HPLC-MS system. The main characteristic MS peak at 814.85, corresponding to (MInsP6+7Na)+. The molar mass of InsP6 is 660.029 g·mol−1. (B) PA200 was validated using the same program, and the MS gave one characteristic peak at 814.92 corresponding to (MInsP6+7Na)+ (red) and a series of peaks that represent different forms of sodium 5,6[PP]2-InsP4 with various number of Na+ ions, i.e., peak 1,019.19 (M5,6[PP]2-InsP4+9Na)+ (cyan), peak 1,041.13 (M5,6[PP]2-InsP4+10Na)+ (green), and peak 1,063.24 (M5,6[PP]2-InsP4+11Na)+ (blue). 5,6[PP]2-InsP4, (5,6)-bisdiphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate; HPLC-MS, high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry; InsP6, inositol hexakisphosphate; PA200, proteasome activator 200.