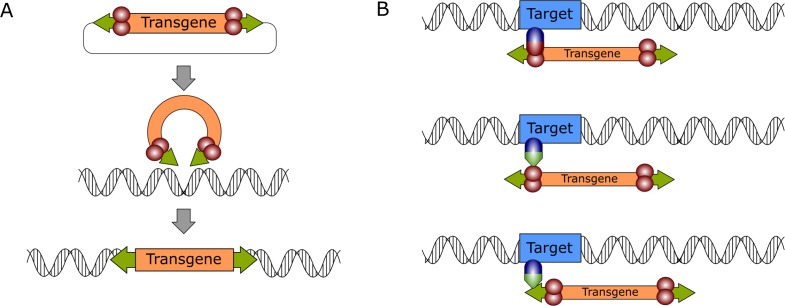
Figure 1. General mechanism of DNA transposition and molecular strategies for targeted gene integration.
(A) The transpositional mechanism of a DNA transposon in a biotechnological context. The transgene, which is flanked by transposon ITRs (green arrows) is excised from a plasmid by the transposase enzyme (red spheres), which is supplied in trans. The genetic cargo is then integrated in the target genome. (B) Transposition can be retargeted by foreign factors that can be DNA-binding domains (blue spheres) directly fused to the transposase or to adapter domains (green triangles) that interact either with the transposase (middle) or the transposon DNA (bottom).