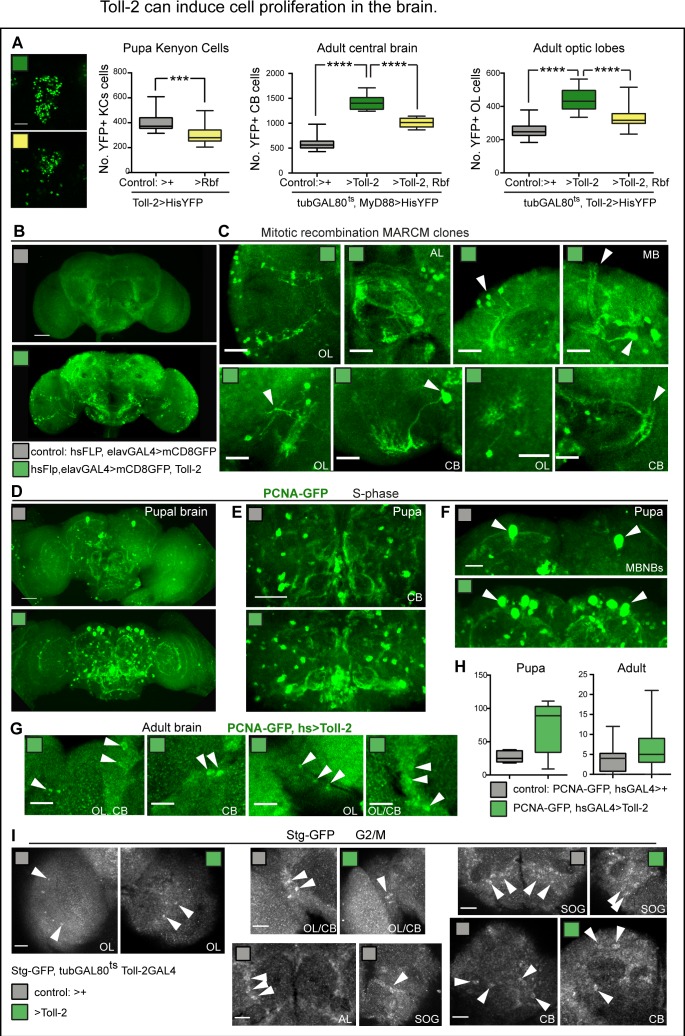
Figure 5. Toll-2 can induce cell proliferation in the brain.
(A) Toll-2 induces G1/S cycling. Over-expression of the G1/S inhibitor Rbf280 in Toll-2+ cells reduced Toll-2 >his-YFP+ KC cell number by day one pupa, compared to controls, meaning that Toll-2+ is required for MB neuroblast divisions. Left box-plot graph: Mann Whitney U test p=0.0004. Middle graph: Conditional over-expression of Rbf280 with tubGAL80ts, MyD88GAL4 at the adult critical period rescued the increase in cell number caused by Toll-2 gain of function, in central brain and optic lobes, meaning that Toll-2 induced cell division. Middle and right box-plot graphs: One Way ANOVA p<0.0001, and post-hoc Bonferroni multiple comparisons corrections. (B,C) Toll-2 induced cell division. Mitotic recombination MARCM clones: no clones were found in control brains (B, n = 17), whereas over-expressing Toll-2 only at the adult critical period resulted in ectopic neurons with differentiated neurites projecting in multiple brain domains (B, C n = 4/17 brains). (D–H) Toll-2 induces G1/S cycling: Conditional over-expression of Toll-2 with hsGAL4 increased the number of cells with the S-phase marker PCNA-GFP in pupal brains, compared to controls, albeit not significantly. (E,F) Note particularly more PCNA-GFP+ cells in central brain and mushroom body neuroblasts. (G) PCNA-GFP+ cells were found in adult control brains, and increased with Toll-2 gain of function. (H) Box-plots, quantification showed increases, albeit not statistically significant. (I) Stg-GFP fusion protein revealed cells in G2/M in both control brains and brains over-expressing Toll-2 (arrowheads). AL: antennal lobe; OL: optic lobe; CB: central brain; SOG: sub-esophageal ganglion. Scale bars: A,B,D,E: 50 μm; C,F,G,I: 25 μm. For sample sizes, genotypes and statistical details, see Supplementary file 2. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001.