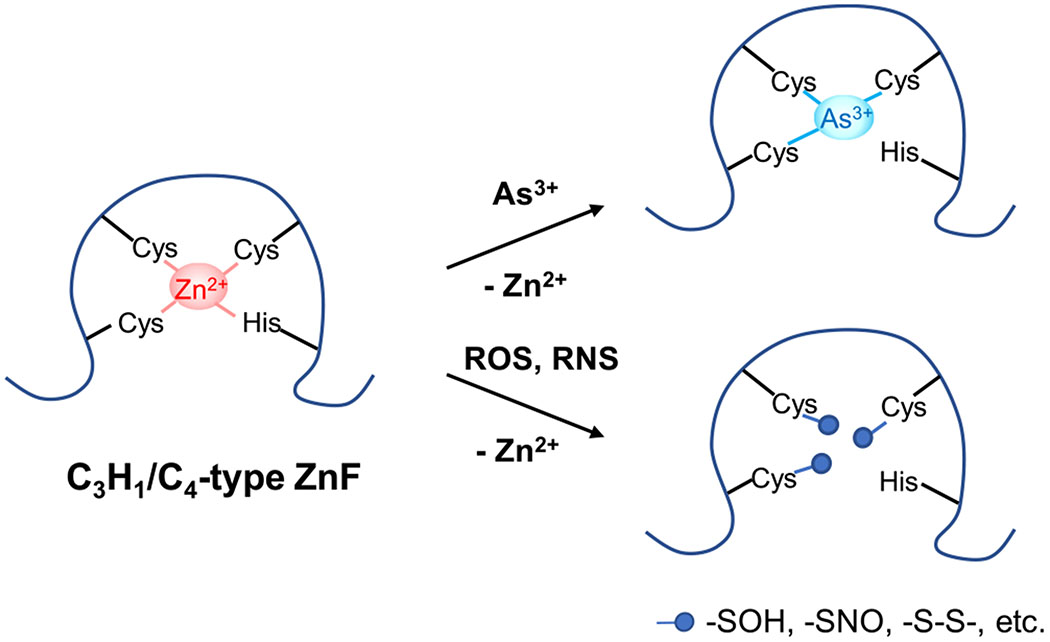
Figure 4.
Modes of action of inorganic arsenic and iAs-induced ROS/RNS in impairing the enzymatic activity of zinc finger (ZnF) proteins. iAs and ROS/RNS can target vicinal cysteines within the zinc coordination spheres of zinc finger proteins: (i) As3+ directly binds to these cysteines more strongly than Zn2+; (ii) ROS oxidizes these cysteines to form a series of oxidization products, such as –SOH and –S–S–; (iii) RNS, especially peroxynitrite, can S-nitrosylate these cysteines. In all these cases, Zn2+ bound within zinc finger motifs is released through its displacement by As3+, which alters the conformation of zinc finger proteins and hence their enzymatic activities.