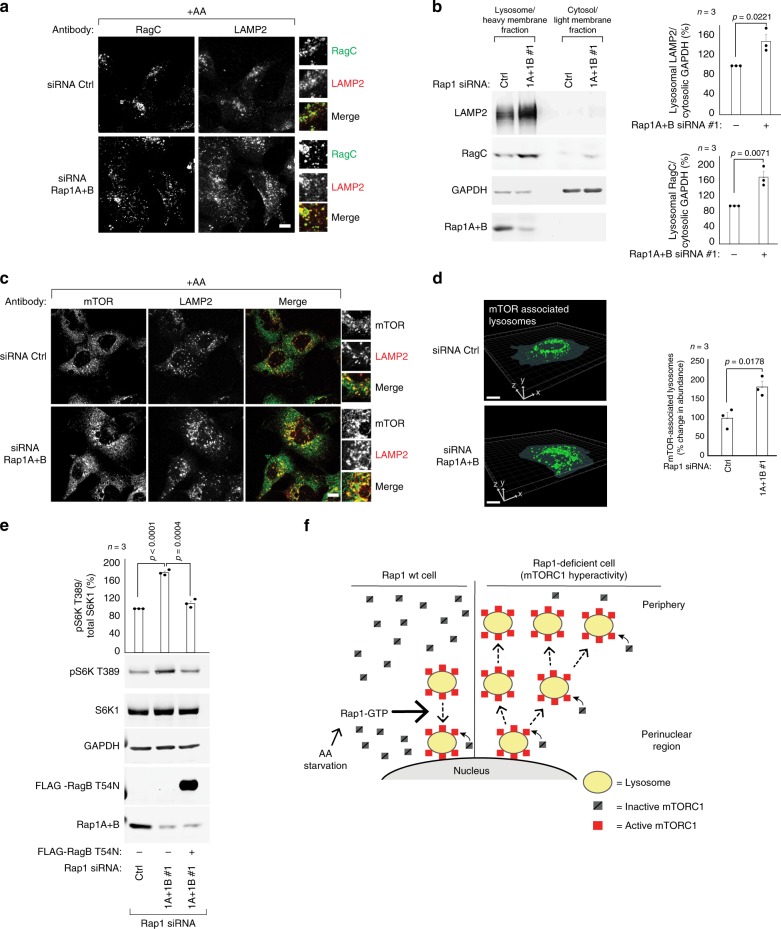
Fig. 5. Rap1 depletion increases the interaction between mTORC1 and lysosomes.
a Immunofluorescence images from a single confocal plane of Rap1A+B-depleted HEK293A cells. Samples were coimmunostained for RagC (green) and LAMP2 (red). b Lysates from control or Rap1A+B siRNA-depleted HEK293A cells were separated into lysosome-enriched heavy membranes and cytosolic/light membranes fractions, and analyzed by immunoblotting for the endogenous amounts of the indicated proteins. Graph shows quantification of lysosome fraction. c, d Samples were processed as in a and coimmunostained for mTOR (green) and LAMP2 (red). The relative change in mTOR-associated lysosomes was quantified using 3D-reconstruction analysis (d). The number of cells analyzed to quantify lysosome abundance is shown in Supplementary Fig. 14. e S6K1 phosphorylation in Rap1-depleted cells expressing dominant negative RagB-T54N cDNA to prevent mTOR localization to lysosomes. f Model: Rap1 suppresses lysosome abundance and peripheral expansion when amino acids are limited (left). When nutrient levels are sufficient, mTORC1 is recruited to and activated on lysosomes (left and right). Rap1 depletion leads to an aberrant increase in lysosomes and the surface available for mTORC1 activation. The enhanced association between mTORC1 and its lysosome-bound activators results in mTORC1 hyperactivity (right). Also, see Supplementary Fig. 13g. The microscopic fields imaged were randomly selected. All experiments were repeated at least three times and graphs represent relative immunoblot band intensity from n individual experiments. Statistical data are presented as mean values ± s.e.m; Student’s t-test; two-sided, unpaired. Scalebars:10 μm. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 17. pS6K T389 and total S6K1 were processed on separate blots due to technical reasons. See Data Source File for statistics source data.